S.I. No. 344/1995 -- European Communities (General Provisions on The Control of Additives, and in Particular Colours and Sweeteners For Use in Foodstuffs) Regulations, 1995.
1995
344
|
|
S.I. No. 344/1995:
EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES (GENERAL PROVISIONS ON THE CONTROL OF ADDITIVES, AND IN PARTICULAR COLOURS AND SWEETENERS FOR USE IN FOODSTUFFS) REGULATIONS, 1995.
|
|
|
EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES (GENERAL PROVISIONS ON THE CONTROL OF ADDITIVES, AND IN PARTICULAR COLOURS AND SWEETENERS FOR USE IN FOODSTUFFS) REGULATIONS, 1995.
|
|
|
The Minister for Health in exercise of the powers conferred on him by Section 3 of the European Communities Act, 1972 (No. 27 of 1972) hereby makes the following Regulations for the purpose of giving effect to:
|
|
|
Council Directive 89/107/EEC(1) on the approximation of the laws of the Member States concerning food additives authorised for use in foodstuffs intended for human consumption.
|
|
|
(1)O.J. No. L40, 11.2.89, pp 27-33
|
|
|
European Parliament and Council Directive 94/35/EC(2) on sweeteners for use in foodstuffs.
|
|
|
(2)O.J. No. L237, 10.9.94, pp 3-12
|
|
|
European Parliament and Council Directive 94/36/EC(3) on colours for use in foodstuffs.
|
|
|
(3)O.J. No. L237, 10.9.94, pp 13-29
|
|
|
Commission Directive 95/31/EC(4) laying down specific criteria of purity concerning sweeteners for use in foodstuffs.
|
|
|
(4)O.J. No. L178, 28.7.95, pp 1-19
|
|
|
Commission Directive 95/45/EC(5) laying down specific purity criteria concerning colours for use in foodstuffs.
|
|
|
(5)O.J. No. L226, 22.9.95, pp 1-45
|
|
|
1. These Regulations may be cited as the European Communities (General Provisions on the Control of Additives, and in particular Colours and Sweeteners for use in Foodstuffs) Regulations, 1995.
|
|
|
2. These Regulations shall come into force on the 31st day of December, 1995.
|
|
|
3. In these Regulations words and phrases shall, except where otherwise indicated, be construed as a reference to an article contained in these Regulations or, as may be, to the Schedule thereto; any reference in an article to a sub-article shall be construed as a reference to a sub-article of that article.
|
|
|
PART I GENERAL PROVISIONS ON FOOD ADDITIVES
|
|
|
4. (1) Subject to sub-article (3) of this article, these Regulations shall apply to all food additives coming within the various categories of food additives listed in Schedule I and which are used or intended to be used as ingredients during the manufacture or preparation of a foodstuff and are still present in the final product, even if in altered form, hereinafter called "food additives".
|
|
|
(2) For the purposes of these Regulations "food additive" means any substance not normally consumed as a food in itself and not normally used as a characteristic ingredient of food whether or not it has nutritive value, the intentional addition of which to food for a technological purpose in the manufacture, processing, preparation, treatment, packaging, transport or storage of such food results, or may be reasonably expected to result, in it or its by-products becoming directly or indirectly a component of such foods.
|
|
|
(3) These regulations shall not apply to:
|
|
|
( a ) processing aids;
|
|
|
( b ) substances used in the protection of plants and plant products in conformity with Community rules relating to plant health;
|
|
|
( c ) flavourings for use in foodstuffs for human consumption in accordance with EC (Flavourings for use in Foodstuffs for Human Consumption) Regulations, 1992 ( S.I. No. 22 of 1992 ).
|
|
|
( d ) substances added to foodstuffs as nutrients (for example, minerals, trace elements or vitamins).
|
|
|
5. ( a ) For the purposes of these Regulations, "processing aid" means any substance not consumed as a food ingredient by itself, intentionally used in the processing of raw materials, food or their ingredients, to fulfil a certain technological purpose during treatment or processing and which may result in the unintentional but technically unavoidable presence of residues of the substance or its derivatives in the final product, provided that these residues do not present any health risk and do not have any technological effect on the finished product.
|
|
|
( b ) The term "quantum satis" when used in the Schedule to these Regulations means that no maximum level is specified. However, the additives in question shall be used in accordance with good manufacturing practice, at a level not higher than is necessary to achieve the intended purpose and provided that they do not mislead the consumer.
|
|
|
( c ) For the purposes of these Regulations "unprocessed" means not having undergone any treatment resulting in a substantial change in the original state of the foodstuffs. However, they may have been, for example, divided, parted, severed, boned, minced, skinned, pared, peeled, ground, cut, cleaned, trimmed, deep-frozen, frozen, chilled, milled or husked, packed or unpacked.
|
|
|
( d ) For the purposes of these Regulations:
|
|
|
(i) the word "infant(s)" shall mean a child/ children under the age of twelve months;
|
|
|
(ii) the words "young children" shall mean children aged between one and three years.
|
|
|
( e ) For the purposes of these Regulations the term "import" shall be construed to mean "from any place outside the European Union".
|
|
|
( f ) For the purposes of these Regulations "sell" shall be construed to include possess for sale or offer, expose or advertise for sale, and "sale" shall be construed accordingly.
|
|
|
6. Where the Minister for Health is of the view that the use or intended use in foodstuffs of any food additive, although complying with these Regulations, endangers human health he may take appropriate measures including the temporary suspension or restriction of trade in that food or food additive in order to protect public health.
|
|
|
7. (1) Food additives not intended for sale to the ultimate consumer shall not be marketed, imported, manufactured, sold, distributed, offered or kept for sale, unless their packaging or containers bear the following information, which must be conspicuous, clearly legible and indelible;
|
|
|
( a ) (i) in the case of food additives sold singly or mixed with each other, for each additive, the name laid down by any regulation made by the Minister for Health and its EEC number or, in the absence of such regulations, a description of the additive that is sufficiently precise to enable it to be distinguished from additives with which it could be confused, in descending order of the proportion by weight in the total;
|
|
|
(ii) when other substances or materials or food ingredients to facilitate storage, sale, standardisation, dilution or dissolution of a food additive or food additive are incorporated in the additives, the name of the additive in accordance with subarticle (1) (a) (i) and an indication of each component in descending order to the proportion by weight in the total.
|
|
|
( b ) either the statement "for use in food" or the statement "restricted use in food", or a more specific reference to its intended food use;
|
|
|
( c ) if necessary, the special conditions of storage and use;
|
|
|
( d ) directions for use, if the omission thereof would preclude appropriate use of the additive;
|
|
|
( e ) a mark identifying the batch or lot;
|
|
|
( f ) the name or business name and address of the manufacturer or packer, or of a seller established within the European Economic Community;
|
|
|
( g ) an indication of the percentage of any component which is subject to a quantitative limitation in a food or adequate compositional information to enable the purchaser to comply with any European Economic Community provisions applying to the food. Where the same quantitive limitation applies to a group of components used singly or in combination, the combined percentage may be given as a single figure;
|
|
|
( h ) the net quantity.
|
|
|
(2) By way of derogation from paragraph 1, the information required in sub-article (1) (a) (ii) and sub-article (1) (d) to (g), may appear merely on the documents relating to the consignment which are to be supplied with or prior to the delivery, provided that the indication "intended for manufacture of foodstuffs and not for retail sale" appears on a conspicuous part of the packaging or container of the product in question.
|
|
|
8. Food additives intended for sale to the ultimate consumer shall not be marketed, imported, distributed, manufactured, sold or offered for sale, unless their packaging or containers bear the following information which must be conspicuous, clearly legible and indelible.
|
|
|
( a ) the name under which the product is sold (this name shall be constituted by the name laid down by any Regulation made by the Minister for Health in relation to the product in question plus its EEC number or, in the absence of such provisions, by a description of the product that is sufficiently precise to enable it to be distinguished from products with which it could be confused);
|
|
|
( b ) the information required by article 7 (1) (a) to (f) and (h);
|
|
|
( c ) the date of minimum durability within the meaning of the Council Directive 79/112/EEC(1), as amended.
|
|
|
OJ No. L33, 8.2.1979, page 1
|
|
|
9. (1) Articles 7 and 8 of these Regulations shall not affect more detailed or more extensive laws, regulations or administrative provisions regarding weights and measures, or applying to the presentation, classification, packaging and labelling of dangerous substances and preparations or the transport of such substances.
|
|
|
(2) The particulars required by articles 7 and 8 shall be given in the Irish or English languages unless other measures have been taken to ensure that the purchaser is informed. The provision shall not prevent such particulars from also being indicated in various other languages.
|
|
|
10. (1) A person shall not import, manufacture, sell, distribute, or offer for sale or keep for sale, food additives except in conformance with these Regulations.
|
|
|
(2) However, and where appropriate, Article 20 may be relied upon by way of derogation from sub-article (1) of this Article.
|
|
|
PART II SWEETENERS FOR USE IN FOODSTUFFS
|
|
|
11. (1) For the purposes of these Regulations, the term "sweeteners" refers to food additives which are used:
|
|
|
-- to impart a sweet taste to foodstuffs
|
|
|
-- as table-top sweeteners
|
|
|
These Regulations do not apply to foodstuffs with sweetening properties.
|
|
|
(2) A sweetener listed in Schedule II to these Regulations must satisfy the purity criteria for that sweetener as set out in Schedule III laying down specific criteria of purity concerning sweeteners for use in foodstuffs.
|
|
|
(3) For the purpose of these Regulations, "with no added sugar" and 'energy-reduced' in column III of Schedule II shall be defined as follows:
|
|
|
--'with no added sugar': without any added mono-or disaccharides or any other foodstuff used for its sweetening properties;
|
|
|
--'energy-reduced': with an energy value reduced by at least 30% compared with the original foodstuff or a similar product.
|
|
|
12. (1) Only those sweeteners listed in Schedule II may be placed on the market with a view to:
|
|
|
--sale to the ultimate consumer; or
|
|
|
--use in the manufacture of foodstuffs.
|
|
|
(2) Sweeteners referred to in the second indent of sub-article (1) may only be used in the manufacture of the foodstuffs listed in Schedule II under the conditions specified therein.
|
|
|
(3) Except where specifically provided for, sweeteners may not be used in foods for infants or young children, as specified in the Health (Foods for Particular Nutritional Uses) Regulations, 1991 ( S.I. No. 331 of 1991 ).
|
|
|
(4) The maximum usable doses indicated in Schedule II refer to ready-to-eat foodstuffs prepared according to the instructions for use.
|
|
|
13. (1) These Regulations shall apply without prejudice to any other Regulations permitting additives listed in Schedule II to be used for purposes other than sweetening.
|
|
|
(2) These Regulations shall also apply without prejudice to national or Community provisions governing the composition and the description of foodstuffs.
|
|
|
14. (1) The sale description of a table-top sweetener must include the term 'x based table-top sweetener', where 'x' is the name(s) of the sweetening substances(s) used in its composition.
|
|
|
(2) The labelling of a table-top sweetener containing polyols and/or aspartame must bear the following warnings:
|
|
|
--polyols: `excessive consumption may induce laxative effects',
|
|
|
--aspartame: `contains a source of phenylalanine'.
|
|
|
PART III COLOURS FOR USE IN FOODSTUFFS
|
|
|
15. (1) For the purposes of these Regulations, 'colours' are substances which add or restore colour in a food, and include natural constituents of foodstuffs and natural sources which are normally not consumed as foodstuffs as such and not normally used as characteristic ingredients of food.
|
|
|
Preparations obtained from foodstuffs and other natural source materials obtained by physical and/or chemical extraction resulting in a selective extraction of the pigments relative to the nutritive or aromatic constituents are colours within the meaning of these Regulations.
|
|
|
The following substances shall not be considered colours for the purposes of these Regulations.
|
|
|
(i) foodstuffs, whether dried or in concentrated form and flavourings incorporated during the manufacturing of compound foodstuffs, because of their aromatic, sapid or nutritive properties together with a secondary colouring effect, such as paprika, turmeric and saffron.
|
|
|
(ii) colours used for the colouring of the inedible external parts of foodstuffs, such as cheese coatings and sausage casings.
|
|
|
(2) Only the substances listed in Schedule IV, Part A may be used as colours in foodstuffs.
|
|
|
(3) Colours may be used only in the foodstuffs listed in Schedule IV, Part C, D and E and under the conditions specified therein; colours may be used in those same foodstuffs when they are intended for particular uses in accordance with Health (Foods for Particular Nutritional Uses) Regulations, 1991 ( S.I. No. 331 of 1991 ).
|
|
|
(4) Colours may not be used in the foodstuffs listed in Schedule IV, Part B except where specifically provided for in Schedule IV, Part C, Part D or Part E.
|
|
|
(5) Colours permitted for certain uses only are listed in Schedule IV, Part D.
|
|
|
(6) Colours permitted in general in foodstuffs and the conditions of use therefor are listed in Schedule IV, Part E.
|
|
|
(7) The maximum levels indicated in Schedule IV to these Regulations
|
|
|
(i) relate to ready-to-eat foodstuffs, prepared according to the instructions for use,
|
|
|
(ii) refer to the quantities of colouring principle contained in the colouring preparation.
|
|
|
(8) For the purpose of health marking as provided in Directive 9¼97/EEC(1) and other marking required on meat products, only E155 Brown HT, E133 Brilliant Blue FCF or E129 Allura Red AC or an appropriate mixture of E133 Brilliant Blue FCF and E129 Allura Red AC may be used.
|
|
|
(1)OJ No. L268, 24.9.1991, p. 69
|
|
|
(9) Only those colours mentioned in Schedule IV, Part A may be used for the decorative colouring of eggshells or for the stamping of eggshells as provided in Regulations (EEC) No. 1274/91(2).
|
|
|
(2)OJ No. L121, 16.5.1991, p. 11
|
|
|
(10) Only those colours listed in Schedule IV, Part A, except E123, E127, E128, E154, E160b, E161g, E173 and E180 may be sold directly to consumers.
|
|
|
(11) A colour listed in Schedule IV to these Regulations must satisfy the purity criteria for that colour as set out in Schedule V, laying down specific criteria of purity concerning colours for use in foodstuffs.
|
|
|
16. Without prejudice to other European Community provisions, the presence of a colour in a foodstuff is permissible:
|
|
|
(i) in a compound foodstuff other than one mentioned in Schedule IV, Part B to the extent that the colour is permitted in one of the ingredients of the compound foodstuff;
|
|
|
(ii) if the foodstuff is destined to be used solely in the preparation of a compound foodstuff and to such an extent that the compound foodstuff conforms to the provisions of these Regulations.
|
|
|
PART IV FINAL PROVISIONS
|
|
|
17. ( a ) These Regulations shall be enforced and executed by each health board, established in accordance with the Health Act 1970 (No. 1 of 1970) in respect of its functional area through its authorised officers and/or the officers of the Minister for Health who are authorised officers for the purposes of these Regulations.
|
|
|
( b ) For the purposes of these Regulations, "authorised officer" means
|
|
|
( a ) an officer of the Minister for Health who is authorised in writing by the Minister for Health to be an authorised officer for the purposes of these Regulations; or
|
|
|
( b ) an officer of a health board who is authorised in writing by the Chief Executive Officer of the health board to be an authorised officer for the purposes of these Regulations.
|
|
|
18. (1) Where an authorised officer reasonably suspects or believes that a foodstuff or food additive does not comply with these regulations, the authorised officer may seize, remove and/or detain such foodstuffs or food additive as being a foodstuff or food additive which is unfit for human consumption.
|
|
|
(2) With the consent in writing of the owner or person responsible for such foodstuff or food additive, an authorised officer may destroy or otherwise dispose of it so as to prevent its use for human consumption.
|
|
|
(3) An authorised officer who has seized any foodstuff or food additive in pursuance of the provisions of this article may, on giving notice in writing to the owner or person responsible for such foodstuff or food additive apply to a Judge of the District Court for an Order directing that such food or food additive be destroyed or otherwise disposed of as being a foodstuff or food additive which is unfit for human consumption.
|
|
|
(4) A Judge of the District Court to whom the application is made for an Order under sub-article (3) of this article shall, if satisfied that such foodstuff or food additive does not comply with these Regulations, order that it be destroyed or otherwise disposed of after such period, not exceeding fourteen days, as may be specified in such order, as being a foodstuff or food additive which is unfit for human consumption and an officer shall destroy or dispose of it accordingly.
|
|
|
19. A person shall give to any authorised officer all reasonable assistance that the officer may require in the performance of his duties under these Regulations and such assistance shall include the giving of information relating to the composition and use of any foodstuff or food additive and the identity of the person from whom or the place from which any such foodstuff or food additive has been obtained and the person to whom and the place to which it has been consigned or the manner in which it has been consigned or the manner in which it has otherwise been disposed of.
|
|
|
20. In any proceedings for an offence under these Regulations it shall be a defence for the person charged to show that the food in respect of which the offence is alleged to have been committed was intended for export and complied with the domestic food legislation of the importing country relevant to the alleged offence.
|
|
|
21. (1) Any person who contravenes any Article or Sub Article of these Regulations shall be guilty of an offence.
|
|
|
(2) A person guilty of an offence under the Regulations shall be liable on summary conviction to a fine not exceeding £1,000 or at the discretion of the Court, to imprisonment for a term not exceeding 6 months or to both.
|
|
|
(3) Where an offence under these Regulations is committed by a body corporate and is proved to have been so committed with the consent or connivance of or to be attributable to any neglect on the part of a director, manager, secretary or other officer of the body corporate, the director, manager, secretary or other officer or any person purporting to act in such capacity shall, as well as the body corporate, be guilty of an offence and shall be liable to be proceeded against and punished accordingly.
|
|
|
(4) Notwithstanding section 10 (4) of the Petty Sessions (Ireland) Act, 1851, proceedings for an offence under these Regulations may be instituted within 12 months from the date of the offence.
|
|
|
22. An offence under these Regulations shall be prosecuted by the Minister for Health or by a health board in whose functional area the offence was committed.
|
|
|
23. The following Regulations are hereby revoked:--
|
|
|
Health (Colouring Agents in Food) Regulations, 1973 ( S.I. No. 149 of 1973 ),
|
|
|
Health (Colouring Agents in Food) (Amendment) Regulations, 1978 ( S.I. No. 140 of 1978 ).
|
|
|
Health (Colouring Agents in Food) (Amendment) Regulations, 1981 (S.I. No. 336 of 1981),
|
|
|
Health (Colouring Agents in Food) (Amendment) Regulations, 1992 ( S.I. No. 68 of 1992 ),
|
|
|
Health (Cyclamate in Food) Regulations, 1970 ( S.I. No. 49 of 1970 ),
|
|
|
Health (Cyclamate in Food) (Amendment) Regulations, 1992 ( S.I. No. 73 of 1992 ), and
|
|
|
European Communities (Labelling of Additives for use in Foodstuffs) Regulations, 1992 ( S.I. No. 23 of 1992 ).
|
|
|
SCHEDULES
|
|
|
SCHEDULE I
|
|
|
Categories of Food Additives
|
|
|
SCHEDULE II
|
|
|
Sweeteners for use in Foodstuffs
|
|
|
SCHEDULE III
|
|
|
Specific Criteria of Purity concerning Sweeteners for use in foodstuffs
|
|
|
SCHEDULE IV
|
|
|
List of Permitted Food Colours
|
|
|
SCHEDULE II
|
|
|
Specific Purity Criteria concerning Colours for use in Foodstuffs
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SCHEDULE I
|
|
|
Categories of Food Additives
|
|
|
Colour
|
|
|
Preservative
|
|
|
Anti-oxidant
|
|
|
Emulsifier
|
|
|
Emulsifying salt
|
|
|
Thickener
|
|
|
Gelling agent
|
|
|
Stabilizer(1)
|
|
|
Flavour enhancer
|
|
|
Acid
|
|
|
Acidity regulator(2)
|
|
|
Anti-caking agent
|
|
|
Modified starch
|
|
|
Sweetener
|
|
|
Raising agent
|
|
|
Anti-foaming agent
|
|
|
Glazing agent(3)
|
|
|
Flour treatment agent
|
|
|
Firming agent
|
|
|
Humectant
|
|
|
Sequestrant(4)
|
|
|
Enzyme(4) (5)
|
|
|
Bulking agent
|
|
|
Propellent gas and packaging gas
|
|
|
(1)This category also comprises foam stabilizers.
|
|
|
(2)These can act as two-way acidity regulators.
|
|
|
(3)These substances include lubricants.
|
|
|
(4)Inclusion of these terms in this list is without prejudice to any future decision or mention thereof in the labelling of foodstuffs intended for the final consumer.
|
|
|
(5) Only those used as additives.
|
|
|
SCHEDULE II
|
|
|
Sweeteners for use in Foodstuffs
|
|
|
|
|
|
| EC No. |
Name |
Foodstuffs |
Maximum usable dose |
| E420 |
Sorbitol |
Desserts and similar products |
quantum satis |
|
(i) Sorbital |
|
|
|
(ii) Sorbital syrup |
|
|
| E421 |
Mannitol |
--Water-based flavoured desserts, energy-reduced or with no added |
|
| E953 |
Isomalt |
sugar |
|
| E965 |
Maltitol |
--Milk and milk-derivative-based preparations, energy-reduced or with |
|
|
(i) Maltitol |
no added sugar |
|
|
(ii) Maltitol syrup |
--Fruit- and vegetable-based desserts, energy-reduced or with no added |
|
| E966 |
Lactitol |
sugar |
|
| E967 |
Xylitol |
--Egg-based desserts, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
|
|
|
--Cereal-based desserts, energy reduced or with no added sugar |
|
|
|
--Breakfast cereals or cereal-based products, energy reduced or with no added sugar |
|
|
|
--Fat-based desserts, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
|
|
|
--Edible ices, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
|
|
|
--Jams, jellies, marmalades and crystallized fruit, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
|
|
|
--Fruit preparations, energy-reduced or with no added sugar, with the exception of those intended for the manufacture of fruit-juice-based drinks |
|
|
|
Confectionery |
|
|
|
--Confectionery with no added sugar |
|
|
|
--Dried-fruit-based confectionery, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
|
|
|
--Starch-based confectionery, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 420, E 421, E 953, E 965, E 966, E 967 --contd. |
|
--Cocoa-based products, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
|
|
|
--Cocoa, milk, dried-fruit or fat-based sandwich spreads, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
|
|
|
--Chewing gum with no added sugar |
|
|
|
--Sauces |
|
|
|
--Mustard |
|
|
|
--Fine bakery products, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
|
|
|
--Products intended for particular nutritional uses |
|
|
|
--Solid food
supplements/dietary integrators
|
|
|
E 950
|
Acesulfame K |
Non-alcoholic drinks |
|
|
|
--Water-based flavoured drinks, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
350 mg/l |
|
|
--Milk and milk-derivative-based or fruit-juice-based drinks, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
350 mg/l |
|
|
Desserts and similar products |
|
|
|
--Water-based flavoured desserts, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
350 mg/kg |
|
|
--Milk and milk-derivative-based preparations, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
350 mg/kg |
|
|
--Fruit and vegetable-based desserts, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
350 mg/kg |
|
|
--Egg-based desserts, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
350 mg/kg |
|
|
--Cereal-based desserts, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
350 mg/kg |
|
|
--Fat-based desserts, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
350 mg/kg |
|
|
--'snacks': certain flavours or ready to eat, prepacked, dry, savoury starch products and coated nuts |
350 mg/kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 950--contd. |
|
Confectionery |
|
|
|
--Confectionery with no added sugar |
500 mg/kg |
|
|
--Cocoa- or dried-fruit-based confectionery, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
500 mg/kg |
|
|
--Starch-based confectionery, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
1 000 mg/kg |
|
|
--Cocoa, milk, dried-fruit or fat-based sandwich spreads, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
1 000 mg/kg |
|
|
--Chewing gum with no added sugar |
2 000 mg/kg |
|
|
--Cider and perry |
350 mg/l |
|
|
--Alcohol-free beer or with an alcohol content not exceeding 1,2% vol |
350 mg/l |
|
|
--'Biere de table/Tafelbier/Table Beer' (original wort content less than 6%) except for 'Obergariges Einfachbier' |
350 mg/l |
|
|
--Beers with a minimum acidity of 30 milli-equivalents expressed as NaOH |
350 mg/l |
|
|
--Brown beers of the 'oud bruin' type |
350 mg/l |
|
|
-- Edible ices, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
800 mg/kg |
|
|
--Canned or bottled fruit, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
350 mg/kg |
|
|
--Energy-reduced jams, jellies and marmalades |
1 000 mg/kg |
|
|
--Energy-reduced fruit and vegetable preparations |
350 mg/kg |
|
|
--Sweet-sour preserves of fruit and vegetables |
200 mg/kg |
|
|
--Sweet-sour preserves and semi-preserves of fish and marinades of fish, crustaceans and molluscs |
200 mg/kg |
|
|
--Sauces |
350 mg/kg |
|
|
--Mustard |
350 mg/kg |
|
|
--Fine bakery products for special nutritional uses |
1 000 mg/kg |
|
|
--Complete formulae for weight control intended to replace total daily food intake or an individual meal |
450 mg/kg |
|
|
--Complete formulae and nutritional supplements for use under medical supervision |
450 mg/kg |
|
|
--Liquid food supplements/dietary integrators |
350 mg/l |
|
|
--Solid food supplements/dietary integrators |
500 mg/l |
|
|
--Vitamins and dietary preparations |
2 000 mg/kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 951 |
Aspartame |
Non-alcoholic drinks |
|
|
|
--Water-based flavoured drinks, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
600 mg/l |
|
|
--Milk and milk-derivative-based or fruit-juice-based drinks, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
600 mg/l |
|
|
Desserts and similar products |
|
|
|
--Water-based flavoured desserts, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
1 000 mg/kg |
|
|
--Milk and milk-derivative-based preparations, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
1 000 mg/kg |
|
|
--Fruit and vegetable-based desserts, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
1 000 mg/kg |
|
|
--Egg-based desserts, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
1 000 mg/kg |
|
|
--Cereal-based desserts, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
1 000 mg/kg |
|
|
--Fat-based desserts, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
1 000 mg/kg |
|
|
--'snacks': certain flavours of ready to eat, prepacked, dry, savoury starch products and coated nuts |
500 mg/kg |
|
|
Confectionery |
|
|
|
--Confectionery with no added sugar |
1 000 mg/kg |
|
|
--Cocoa or dried-fruit-based confectionery, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
2 000 mg/kg |
|
|
--Starch-based confectionery, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
2 000 mg/kg |
|
|
--Cocoa-, milk-, dried-fruit or fat-based sandwich spreads, energy reduced or with no added sugar |
1 000 mg/kg |
|
|
--Chewing gum with no added sugar |
5 500 mg/kg |
|
|
--Cider and perry |
600 mg/l |
|
|
--Alcohol-free or with an alcohol content not exceeding 1,2% vol |
600 mg/l |
|
|
--'Biere de table/Tafelbier Beer' (original wort content less than 6%) except for 'Obergariges Einfachbier' |
600 mg/l |
|
|
--Beers with a minimum acidity of 30 milli-equivalents expressed as NaOH |
600 mg/l |
|
|
--Brown Beers of the 'oud bruin' type |
600 mg/l |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 951--contd. |
|
--Edible ices, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
800 mg/kg |
|
|
--Canned or bottled fruit, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
1 000 mg/kg |
|
|
--Energy-reduced jams, jellies and marmalades |
1 000 mg/kg |
|
|
--Energy-reduced fruit and vegetable preperations |
1 000 mg/kg |
|
|
--Sweet-sour preserves of fruit and vegetables |
300 mg/kg |
|
|
--Sweet-sour preserves and semi-preserves of fish and marinades of fish, crustaceans and molluscs |
300 mg/kg |
|
|
--Sauces |
350 mg/kg |
|
|
--Mustard |
350 mg/kg |
|
|
--Fine bakery products for special nutritional uses |
1 700 mg/kg |
|
|
--Complete formulae for weight control intended to replace total daily food intake or an individual meal |
800 mg/kg |
|
|
--Complete formulae and nutritional supplements for use under medical supervision |
1 000 mg/kg |
|
|
--Liquid food supplements/dietary integrators |
600 mg/kg |
|
|
--Solid food supplements/dietary integrators |
2 000 mg/kg |
|
|
Vitamins and dietary preperations |
5 500 mg/kg |
| E 952 |
Cyclamic acid and its Na and Ca salts |
Non-alcoholic drinks |
|
|
|
--Water-based flavoured drinks, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
400 mg/l |
|
|
--Milk and milk-derivative-based or fruit-juice-based drinks, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
400 mg/l |
|
|
Desserts and similar products |
|
|
|
--Water-based flavoured desserts, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
250 mg/kg |
|
|
--Milk-and milk-derivative-based preparations, energy-reduced or with no sugar added |
250 mg/kg |
|
|
--Fruit-and vegetable-based desserts, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
250 mg/kg |
|
|
--Egg-based desserts, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
250 mg/kg |
|
|
--Cereal-based desserts, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
250 mg/kg |
|
|
--Fat-based desserts, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
250 mg/kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 952--contd. |
|
Confectionery |
|
|
|
--Confectionery with no added sugar |
500 mg/kg |
|
|
--Cocoa or dried-fruit-based confectionery, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
500 mg/kg |
|
|
--Starch-based confectionery, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
500 mg/kg |
|
|
--Cocoa, milk, dried-fruit or fat-based sandwich spreads, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
500 mg/kg |
|
|
--Chewing gum with no added sugar |
1 500 mg/kg |
|
|
--Edible ices, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
250 mg/kg |
|
|
--Canned or bottled fruit, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
1 000 mg/kg |
|
|
--Energy-reduced jams, jellies, and marmalades |
1 000 mg/kg |
|
|
--Energy-reduced fruit and vegetable preparations |
250 mg/kg |
|
|
--Fine bakery products for special nutritional uses |
1 600 mg/kg |
|
|
--Complete formulae for weight control intended to replace total daily food intake or an individual meal |
400 mg/kg |
|
|
--Complete formulae and nutritional supplements for use under medical supervision |
400 mg/kg |
|
|
--Liquid food supplements/dietary integrators |
400 mg/kg |
|
|
--Solid food supplements/dietary integrators |
500 mg/kg |
| E 954 |
Saccharin and its Na, K and Ca salts |
Non-alcoholic drinks |
|
|
|
--Water-based flavoured drinks, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
80 mg/l |
|
|
--Milk-and milk-derivative-based or fruit-based drinks, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
80 mg/l |
|
|
--'Gaseosa': non-alcoholic water-based drink with added carbon dioxide, sweeteners and flavourings |
100 mg/l |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 954--contd. |
|
Desserts and similar products |
|
|
|
--Water-based flavoured desserts, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
100 mg/kg |
|
|
--Milk-and milk-derivative-based preperations, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
100 mg/kg |
|
|
--Fruit and vegetable-based desserts, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
100 mg/kg |
|
|
--Egg-based desserts, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
100 mg/kg |
|
|
--Cereal-based desserts, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
100 mg/kg |
|
|
--Fat-based desserts, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
100 mg/kg |
|
|
--'snacks': certain flavours of ready to eat, prepacked, dry savoury starch products and coated nuts |
100 mg/kg |
|
|
Confectionery |
|
|
|
--Confectionery with no added sugar |
500 mg/kg |
|
|
--Cocoa-or dried-fruit-based confectionery, energy reduced or with no added sugar |
500 mg/kg |
|
|
--Starch-based confectionery, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
300 mg/kg |
|
|
--Essoblaten |
800 mg/kg |
|
|
--Cocoa-, milk, dried-fruit or fat-based sandwich spreads, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
200 mg/kg |
|
|
--Chewing gum with no added sugar |
1 200 mg/kg |
|
|
--Cider and perry |
80 mg/l |
|
|
--Alcohol-free beer or with an alcohol content not exceeding 1.2% vol |
80 mg/l |
|
|
--'Biere de table/Tafelbier/Table beer' (original wort content less than 6%) except 'Obergariges Einfachbier' |
80 mg/l |
|
|
--Beers with a minimum acidity of 30 milli-equivalents expressed as NaOH |
80 mg/l |
|
|
--Brown beers of the 'oud bruin' type |
80 mg/l |
|
|
--Edible ices, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
100 mg/kg |
|
|
--Canned or bottled fruit, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
200 mg/kg |
|
|
--Energy-reduced jams, jellies and marmalades |
200 mg/kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 954 -- contd. |
|
--Energy-reduced fruit and vegetable preperations |
200 mg/kg |
|
|
--Sweet-sour preserves of fruit and vegetables |
160 mg/kg |
|
|
--Sweet-sour preserves and semi-preserves of fish and marinades of fish, crustaceans and molluscs |
160 mg/kg |
|
|
--Sauces |
160 mg/kg |
|
|
--Mustard |
320 mg/kg |
|
|
--Fine bakery products for special nutritional uses |
170 mg/kg |
|
|
--Complete formulae for weight control intended to replace total daily food intake or an individual meal |
240 mg/kg |
|
|
--Complete formulae and nutritional supplements for use under medical supervision |
200 mg/kg |
|
|
--Liquid food supplements/dietary integrators |
80 mg/kg |
|
|
--Solid food supplements/dietary integrators |
500 mg/kg |
|
|
--Vitamins and dietary preparations |
1 200 mg/kg |
| E 957 |
Thaumatin |
Confectionery |
|
|
|
--Confectionery with no added sugar |
50 mg/kg |
|
|
--Cocoa-or dried-fruit-based confectionery, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
50 mg/kg |
|
|
--Chewing gum with no added sugar |
50 mg/kg |
|
|
--Vitamins and dietary preparations |
400 mg/kg |
| E 959 |
Neohesperidine DC |
Non-alcoholic drinks |
|
|
|
--Water based flavoured drinks, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
30 mg/l |
|
|
--Milk and milk-derivative-based drinks, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
50 mg/l |
|
|
--Fruit-juice-based drinks, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
30 mg/l |
|
|
Desserts and similar products |
|
|
|
--Water-based flavoured desserts, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
50 mg/kg |
|
|
--Milk-and milk-derivative-based preparations, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
50 mg/kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E959 -- contd. |
|
--Fruit and vegetable-based desserts, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
50 mg/kg |
|
|
--Egg-based desserts, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
50 mg/kg |
|
|
--Cereal-based desserts, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
50 mg/kg |
|
|
--Fat-based desserts, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
50 mg/kg |
|
|
Confectionery |
|
|
|
--Confectionery with no added sugar |
100 mg/kg |
|
|
--Cocoa or dried-fruit-based confectionery, energy- reduced or with no added sugar |
100 mg/kg |
|
|
--Starch-based confectionery, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
150 mg/kg |
|
|
--Essoblaten |
50 mg/kg |
|
|
--Cocoa-, milk-, dried-fruit or fat-based sandwich spreads, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
50 mg/kg |
|
|
--Chewing gum with no added sugar |
400 mg/kg |
|
|
--Cider and perry |
20 mg/l |
|
|
--Alcohol-free beer or with an alcohol content not exceeding 1.2% vol |
10 mg/l |
|
|
--'Biere de table/Tafelbier/Table beer' (original wort content less than 6%) except 'Obergariges Einfachbier' |
10 mg/l |
|
|
--Beers with a minimum acidity of 30 milli-equivalents expressed as NaOH |
10 mg/l |
|
|
--Brown beers of the 'oud bruin' type |
10 mg/l |
|
|
--Edible ices, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
50 mg/kg |
|
|
--Canned or bottled fruit, energy-reduced or with no added sugar |
50 mg/kg |
|
|
--Energy-reduced jams, jellies and marmalades |
50 mg/kg |
|
|
--Sweet-sour preserves of fruit and vegetables |
100 mg/kg |
|
|
--Energy-reduced fruit and vegetable preparations |
50 mg/kg |
|
|
--Sweet-sour preserves and semi-preserves of fish and marinades of fish, crustaceans and molluscs |
30 mg/kg |
|
|
--Sauces |
50 mg/kg |
|
|
--Mustard |
50 mg/kg |
|
|
--Fine bakery products for special nutritional uses |
150 mg/kg |
|
|
--Complete formulae for weight control intended to replace total daily food intake or an individual meal |
100 mg/kg |
|
|
--Liquid food supplements/dietary integrators |
50 mg/kg |
|
|
--Solid food supplements/dietary integrators |
100 mg/kg |
|
|
|
SCHEDULE III
|
|
|
Specific Criteria of Purity concerning Sweeteners for use in foodstuffs
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 420 (i) -- SORBITOL |
D-glucitol, D-sorbitol
|
| Definition |
|
| Chemical name |
D-glucitol
|
| Einics |
200-061-5
|
| E number |
E 420 (i)
|
| Chemical formula |
C6H14O6
|
| Relative molecular mass |
182,17
|
| Assay |
Content not less than 97% of total glycitols and not less than 91% of D-sorbitol on the dry weight basis.
|
|
Glycitols are compounds with the structural formula CH2OH(CHOH)nCH2OH, where "n" is an integer.
|
| Description |
White hygroscopic powder, cystalline powder, flakes or granules having a sweet taste.
|
| Identification |
|
| A. Solubility |
Very soluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol
|
| B. Melting range |
88 to 102°C
|
| C. Sorbitol monobenzylidene derivative |
To 5g of the sample add 7 ml of methanol, 1ml of benzaldehyde and 1ml of hydrochloric acid. Mix and shake in a mechanical shaker until crystals appear. Filter with the aid of suction, dissolve the crystals in 20ml of boiling water containing 1g of sodium bicarbonate, filter while hot, cool the filtrate, filter with suction, wash with 5ml of methanol-water mixture (1 in 2) and dry in air. The crystals so obtained melt between 173 and 179°C.
|
| Purity |
|
| Water content |
Not more than 1% (Karl Fischer method)
|
| Sulphated ash |
Not more than 0.1% expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Reducing sugars |
Not more than 0.3% expressed as glucose on dry weight basis
|
| Total sugars |
Not more than 1 % expressed as glucose on dry weight basis
|
| Chlorides |
Not more than 50 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Sulphates |
Not more than 100 mg/kg on dry weight basis
|
| Nickel |
Not more than 2 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Lead |
Not more than 1 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Heavy metals |
Not more than 10 mg/kg expressed as Pb on dry weight basis
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 420 (ii) SORBITOL SYRUP |
|
| Synonyms |
D-glucitol syrup
|
| Definition |
|
| Chemical name |
Sorbitol syrup formed by hydrogenation of glucose syrup is composed of D-sorbitol, D-mannitol and hydrogenated saccharides.
|
|
The part of the product which is not D-sorbitol is composed mainly of hydrogenated oligosaccharides formed by the hydrogenation of glucose syrup used as raw material (in which case the syrup is non-crystalising) or mannitol. Minor quantities of glycitols where n 4 may be present. Glycitols are compounds with the structural formula CH2OH-(CHOH)n-CH2OH, where 'n' is an integer
|
| Einics |
270-337-8
|
| E number |
E 420 (ii)
|
| Assay |
Content not less than 69% total solids and not less than 50% of D-sorbitol on the anhydrous basis
|
| Description |
Clear colourless aand sweet tasting aqueous solution |
| Identification |
|
| A. Solubility |
Miscible with water, with glycerol, and with propane -1,2-diol
|
| B. Sorbitol monobenzylidene derivative |
To 5g of the sample add 7 ml of methanol, 1ml of benzaldehyde and 1ml of hydrochloric acid. Mix and shake in a mechanical shaker until crystals appear. Filter with the aid of suction, dissolve the crystals in 20ml of boiling water containing 1g of sodium bicarbonate, filter while hot. Cool the filtrate, filter with suction, wash with 5ml of methanol-water mixture (1 in 2) and dry in air. The crystals so obtained melt between 173 and 179°C.
|
| Purity |
|
|
Water content
|
Not more than 31% (Karl Fischer method)
|
| Sulphated ash |
Not more than 0,1% expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Reducing sugars |
Not more than 0,3% expressed as glucose on dry weight basis
|
| Chlorides |
Not more than 50 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Sulphates |
Not more than 100 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Nickel |
Not more than 2 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Lead |
Not more than 1 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Heavy metals |
Not more than 10 mg/kg expressed as Pb on dry weight basis |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 421 -- MANNITOL |
|
| Synonyms |
D-Mannitol
|
| Definition |
|
| Chemical name |
D-mannitol |
| Einics |
200-711-8
|
| E number |
E 421 |
| Chemical formula |
C6H14O6 |
| Relative molecular mass |
182,2
|
| Assay |
Content not less than 96% D-mannitol on the dried basis |
| Description |
Sweet tasting, white, odourless, cyrstalline powder |
| Identification |
|
| A. Solubility |
Soluble |
| Purity |
|
| Loss on drying |
Not more than 0,3% (105 °C, four hours) |
| pH |
Between 5 and 8 |
|
Add 0,5ml of a saturated solution of potassium chloride to 10ml of a 10% w/v solution of the sample then measure the pH |
| Specific rotation |
α 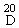
|
|
Specific rotation in a borated solution calculated with reference to the anhydrous substance is between + 23 and + 25° |
| Sulphated ash |
Not more than 0,1% expressed on dry weight basis |
| Reducing sugars |
Not more than 0,3% expressed as glucose on dry weight basis |
| Total sugars |
Not more than 1% expressed as glucose on dry weight basis |
| Chlorides |
Not more than 70 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis |
| Sulphates |
Not more than 100 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis |
| Nickel |
Not more than 2 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis |
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis |
| Lead |
Not more than 1 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis |
| Heavy metals |
Not more than 10 mg/kg expressed as Pb on dry weight basis |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
E 953 -- ISOMALT
|
|
|
Synonyms
|
Hydrogenated isomaltulose, hydrogenated palatinose |
|
Definition
|
|
|
Chemical name
|
Isomalt is a mixture of: |
|
D-glucopyranosyl-1.6-D-glucitol and |
|
D-glucopyranosyl-1.1-D-mannitol |
|
dihydrate |
|
Einics
|
|
|
E number
|
E 953 |
|
Chemical formula
|
D-glucopyranosyl-1.6-D-glucitol: C12H24O11 |
|
D-glucopyranosyl-1,1-D-mannitol
|
|
dihydrate: C12H24O112H2O |
|
Relative molecular mass
|
D-glucopyranosyl-1,6-D-glucitol: 344,32
|
|
D-glucopyranosyl-1,1-D-mannitol |
|
dihydrate: 380,32 |
| Assay |
Content not less than 95% of the mixture of D-glucopyranosyl-1,6-D-glucitol and D-glucopyranosyl-1,1-D-mannitol dihydrate determined on the anhydrous basis |
| Description |
Odourless, white, sweet tasting, crystalline slightly hygroscopic substance |
| Identification |
|
| A. Solubility |
Slightly soluble in water, insoluble in ethanol |
| B. Specific rotation |
α 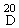 : between + 90 and + 92° : between + 90 and + 92°
(4% w/v solution)
|
| C. Melting range |
145 to 150 °C |
| Tests |
|
| Water content |
Not more than 7% (Karl Fischer method) |
| Sulphated ash |
Not more than 0,05% expressed on dry weight basis |
| Reducing sugars |
Not more than 1,5% expressed as glucose on dry weight basis |
| Nickel |
Not more than 2 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis |
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis |
| Lead |
Not more than 1 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis |
| Heavy metals |
Not more than 10 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 965 (i) -- MALTITOL |
|
| Synonyms |
D-maltitol, hydrogenated maltose |
| Definition |
|
| Chemical name |
(α)-D-glucopyranosyl-1,4-D-glucitol |
| Einics |
209-567-0 |
| E number |
E 965 (i) |
| Chemical formula |
C12H24O11 |
| Relative molecular mass |
344,31 |
| Assay |
Content not less than 98% D-mannitol C12H24O11 on the anhydrous basis |
| Description |
Sweet tasting, white crystalline powder |
| Identification |
|
| A. Solubility |
Very soluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol |
| B. Melting range |
148 to 151 °C |
| C. Specific rotation |
(α)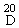 = + 105,5 to + 105,5° (5% w/v solution) = + 105,5 to + 105,5° (5% w/v solution)
|
| Purity |
|
| Water content |
Not more than 1% (Karl Fischer method) |
| Sulphated ash |
Not more than 0,1% expressed on dry weight basis |
| Reducing sugars |
Not more than 0,1% expressed as glucose on dry weight basis |
| Chlorides |
Not more than 50 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis |
| Sulphates |
Not more than 100 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis |
| Nickel |
Not more than 2 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis |
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis |
| Lead |
Not more than 1 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis |
| Heavy metals |
Not more than 10 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 965 (ii) -- MALTITOL SYRUP |
|
| Synonyms |
Hydrogenated high maltose-glucose syrup, hydrogenated glucose syrup |
| Definition |
|
| Chemical name |
A mixture consisting of mainly maltitol with sorbitol and hydrogenated oligo- and polysaccharides. It is manufactured by the catalytic hydrogenation of high maltose-content glucose syrup. The article of commerce is supplied both as a syrup and as a solid product
|
| Einics |
270-337-8
|
| E number |
E 965 (ii)
|
| Assay |
The following ranges apply on the anhydrous basis: |
|
Maltitol not less than 50%
|
|
Sorbitol not more than 8%
|
|
Maltitol not more than 25%
|
|
Hydrogenated polysaccharides containing more than three glucose or glucitol units not more than 30% |
| Description |
Sweet-tasting, colourless and odourless, clear viscous liquids or sweet-tasting white crystalline masses |
|
Identification
|
|
| Description |
|
| Identification |
|
| A. Solubility |
Very soluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol
|
| B. Thin layer chromatography |
Examine by the thin layer chromatography using a plate coated with a 0,25 mm layer of chromatographic silica gel |
| Purity |
|
| Water content |
Not more than 31% (Karl Fischer method)
|
| Sulphated ash |
Not more than 0,1% expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Reducing sugars |
Not more than 0,3% expressed as glucose on dry weight basis
|
| Chlorides |
Not more than 50 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Sulphates |
Not more than 100 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Nickel |
Not more than 2 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Lead |
Not more than 1 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis |
| Heavy metals |
Not more than 10 mg/kg expressed as Pb on dry weight basis |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 966 -- LACTITOL |
|
| Synonyms |
Lactit, lactositol, lactobiosit |
| Definition |
|
| Chemical name |
4-0-ß-D-galactopyranosyl-D-glucitol
|
| Einics |
209-566-5
|
| E number |
E 966
|
| Chemical formula |
C12H24O11
|
| Relative molecular mass |
344,32
|
| Assay |
Not less than 95% on the dry weight basis |
| Description |
Sweet-tasting, crystalline powders or colourless solutions. Crystalline products occur in anhydrous, monohydrate and dihydrate forms |
| Identification |
|
| A. Solubility |
Very soluble in water
|
| B. Specific rotation |
(α) 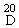 = + 13 to + 16° calculated on the anhydrous basis (10% w/v aqueous solution) = + 13 to + 16° calculated on the anhydrous basis (10% w/v aqueous solution)
|
| Purity |
|
| Water content |
Crystalline products; not more than 10.5% (Karl Fischer method)
|
| Other polyols |
Not more than 2,5% on the anhydrous basis
|
| Reducing sugars |
Not more than 0,2% expressed as glucose on dry weight basis
|
| Chlorides |
Not more than 100 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Sulphates |
Not more than 200 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Sulphated ash |
Not more than 0,1% expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Nickel |
Not more than 2 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Lead |
Not more than 1 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Heavy metals |
Not more than 10 mg/kg expressed as Pb on dry weight basis |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 967 -- XYLITOL |
|
| Synonyms |
Xylitol |
| Definition |
|
| Chemical name |
D-xylitol
|
| Einics |
201-788-0
|
| E number |
E 967
|
| Chemical formula |
C5H12O5
|
| Relative molecular mass |
152,15
|
| Assay |
Not less than 98,5% as xylitol on the anhydrous basis |
| Description |
White, Crystalline Powder, practically odourless with a very sweet taste
|
| Identification |
|
| A. Solubility |
Very soluble in water, sparingly soluble in ethanol
|
| B. Melting range |
92 to 96 °C
|
| C. pH |
5 to 7 (10 w/v aqueous solution) |
| Purity |
|
| Loss on drying |
Not more than 0,5%. Dry 0,5 g of sample in a vacuum over phosphorus at 60 °C for four hours |
| Sulphated ash |
Not more than 0,1% expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Reducing sugars |
Not more than 0,2% expressed as glucose on dry weight basis
|
| Other polyhydric alcohols |
Not more than 1% expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Nickel |
Not more than 2 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Lead |
Not more than 1 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Heavy metals |
Not more than 10 mg/kg expressed as Pb on dry weight basis
|
| Chlorides |
Not more than 100 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Sulphates |
Not more than 200 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 950 -- ACESULFAME K |
|
| Synonyms |
Acesulfame potassium, acesulfam, potassium salt of 3,4-dihydro-6-methyl-1,2,3-oxathiazin-4-one-2,2-dioxide |
| Definition |
|
| Chemical name |
6-methyl-1,2,3-oxathiazin-4(3H)-one-2,2-dioxide potassium salt
|
| Einecs |
259-715-3
|
| E number |
E 950
|
| Chemical formula |
C4H4NO4SK
|
| Relative molecular mass |
201,24
|
| Assay |
Not less than 99% of C4H4NO4SK on the anhydrous basis |
| Description |
Odourless, white, crystalline powder having an intensively sweet taste. Approximately 200 times as sweet as sucrose |
| Identification |
|
| A. Solubility |
Very soluble in water, very slightly soluble in ethanol
|
| B. Ultra-violet absorption |
Maximum 227 ± 2 nm for a solution of 10 mg in 1,000 ml of water |
| Purity |
|
| Loss on drying |
Not more than 1% (105 °C, two hours)
|
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Selenium |
Not more than 30 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Fluoride |
Not more than 3 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Lead |
Not more than 1 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Heavy metals |
Not more than 10 mg/kg expressed as Pb on dry weight basis |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 951 -- ASPARTAME |
|
| Synonyms |
Aspartyl phenylalanine methyl ester |
| Definition |
|
| Chemical name |
N-L-α-(Aspartyl-L-phenylalanine-1-methyl ester, 3-amino-N-(a-carbomethoxy-phenethyl)-succinamic acid-N-methy ester |
| Einecs |
245-261-3
|
| E number |
E 951
|
| Chemical formula |
C14H18N2O5
|
| Relative molecular mass |
294,31
|
| Assay |
Not less than 98% and not more than 102% of C14H18N2O5on the anhydrous basis |
| Description |
White, odourless, crystalline powder having a sweet taste. Approximately 200 times as sweet as Sucrose |
| Identification |
|
| Solubility |
Slightly soluble in water and in ethanol |
| Purity |
|
| Loss on drying |
Not more than 4,5% (105°C, four hours)
|
| Sulphated ash |
Not more than 0,2% expressed on dry weight basis
|
| pH |
Between 4,5 and 6,0 (1 in 125 solution)
|
| Transmittance |
The transmittance of a 1% solution in 2N hydrochloric acid, determined in a 1-cm cell at 430 nm with a suitable spectrophotometer, using 2N hydrochloric acid as a reference, is not less than 0,95, equivalent to an absorbance of not more than approximately 0,022 |
| Specific rotation |
(α) 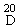 : + 14,5 to + 16,5° : + 14,5 to + 16,5°
Determine in a 4 in 100/15 N formic acid solution within 30 minutes after preparation of the sample solution
|
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Lead |
Not more than 1 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Heavy metals |
Not more than 10 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| 5-Benzyl-3,6-dioxo-2-piperazineacetic acid |
Not more than 1,5% expressed on dry weight basis |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 952 -- CYCLAMIC ACID AND ITS Na AND Ca SALTS |
|
| (I) CYCLAMIC ACID |
|
| Synonyms |
Cyclohexylsulphamic acid, cyclamate |
| Definition |
|
| Chemical name |
Cyclohexanesulphamic acid, cyclohexylaminosulphonic acid
|
| Einecs |
202-898-1
|
| E number |
E 952
|
| Chemical formula |
C6H13NO3 S
|
| Relative molecular mass |
179,24
|
| Assay |
Cyclohexylsulphamic acid contains not less than 98% and not more than the equivalent of 102% of C6H13NO3S, calculated on the anhydrous basis |
| Description |
A practically colourless, white crystalline powder with a sweet-sour taste. Approximately 40 times as sweet as sucrose |
| Purity |
|
| Loss on drying |
Not more than 1% (105°C, one hour)
Not more than 8,5% (140°C, four hours) for the dihydrate form
|
| Selenium |
Not more than 30 mg/kg expressed as selenium on dry weight basis
|
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Lead |
Not more than 1 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Heavy metals |
Not more than 10 mg/kg expressed as Pb on dry weight basis
|
| Cyclohexylamine |
Not more than 10 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Dicyclohexylamine |
Not more than 1 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Aniline |
Not more than 1 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 952 -- CYCLAMIC ACID AND ITS Na AND Ca SALTS--contd. |
|
| (II) SODIUM CYCLAMATE |
|
| Synonyms |
Cyclamate, sodium salt of cyclamic acid |
| Definition |
Sodium cyclohexanesulphamate, sodium cyclohexylsulphamate
|
| Chemical name |
205-348-9
|
| Einecs |
E 952
|
| E number |
C6H12NNaO3S and the dihydrate form C6H12NNaO3S·2H2O
|
| Chemical formula |
201,22 calculated on the anhydrous form
|
| Relative molecular mass |
237,22 calculated on the hydrated form
|
| Assay |
Not less than 98% and not more than 102% on the dried basis Dihydrate form: not less than 84% on the dried basis |
| Description |
White, odourless crystals or crystalline powder. Approximately 30 times as sweet as sucrose |
| Identification |
|
| Solubility |
Soluble in water, practically insoluble in ethanol |
| Purity |
|
| Loss on drying |
Not more than 1% (105°C, one hour) Not more than 15,2% (105°C, two hours) for the dihydrate form |
| Selenium |
Not more than 30 mg/kg expressed as selenium on dry weight basis
|
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Lead |
Not more than 1 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Heavy metals |
Not more than 10 mg/kg expressed as Pb on dry weight basis
|
| Cyclohexylamine |
Not more than 10 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Dicyclohexylamine |
Not more than 1 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Aniline |
Not more than 1 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 952 -- CYCLAMIC ACID AND ITS Na AND Ca SALTS -- contd. |
|
| (III) CALCIUM CYCLAMATE |
|
| Synonyms |
Cyclamate, calcium salt of cyclamic acid |
| Definition |
|
| Chemical name |
Calcium cyclohexanesulphamate, calcium cyclohexylsulphamate
|
| Einecs |
205-349-4
|
| E number |
E 952
|
| Chemical formula |
C12H24 CaN2O6S2·22O
|
| Relative molecular mass |
432,57
|
| Assay |
Not less than 98% and not more than 10% on the dried basis |
| Description |
White, colourless crystals or crystaline powder. Approximately 30 times as sweet as sucrose |
| Identification |
|
| Solubility |
Soluble in water, sparingly soluble in ethanol |
| Purity |
Not more than 1% (105°C, one hour)
|
| Loss on drying |
Not more than 8,5% (140°C, four hours) for the dihydrate form
|
| Selenium |
Not more than 30 mg/kg expressed as selenium on dry weight basis
|
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Lead |
Not more than 1 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Heavy metals |
Not more than 10 mg/kg expressed as Pb on dry weight basis
|
| Cyclohexylamine |
Not more than 10 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Dicyclohexylamine |
Not more than 1 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Aniline |
Not more than 1 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 954 -- SACCHARIN AND ITS Na. K AND Ca SALTS |
|
| (I) SACCHARIN |
|
| Definition |
|
| Chemical name |
3-oxo-2,3dihydrobenzo(d)isothiazol-1,1-dioxide
|
| Einecs |
201-321-0
|
| E number |
E 954
|
| Chemical formula |
C7H5NO3S
|
| Relative molecular mass |
183,18
|
| Assay |
Not less than 99% and not more than 101,0% of C7H5NO3S on the anhydrous basis |
| Description |
White crystals or a white crystalline powder, odourless or with a faint, aromatic odour having a sweet taste even in very dilute solutions. Approximately between 300 and 500 times as sweet as sucrose |
| Identification |
|
| Solubility |
Slightly soluble in water, soluble in basic solutions, sparingly soluble in ethanol |
| Purity |
|
| Loss on drying |
Not more than 1% (105°C, two hours)
|
| Melting range |
226 to 230°C
|
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Selenium |
Not more than 30 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Lead |
Not more than 1 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Heavy metals |
Not more than 10 mg/kg expressed as Pb on dry weight basis
|
| Sulphated ash |
Not more than 0,2% expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Benzoic and salicylic acid |
To 10 ml of a 1 in 20 solution, previously acidified with five drops of acetic acid, add three drops of an approximately molar solution of ferric chloride in water. No precipitate or violet colour appears |
| o-Toluenesulphonamide |
Not more than 10 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| P-Toluenesulphonamide |
Not more than 10 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Benzoic acid p-sulfonamide |
Not more than 25 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Readily carbonizable substances |
Absent |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 954 -- SACCHARIN AND ITS Na. K AND Ca SALTS -- contd. |
|
| (II) SODIUM SACCHARIN |
|
| Synonyms |
Saccharin, sodium salt of saccharin |
| Definition |
|
| Chemical name |
Sodium o-benzosulphimide,
sodium salt of 2,3-dihydro-3-oxobenzisosulfonazole,
oxobenzisosulfonazole,
1,2-benzisotfhiazolin-3-one-1,
1-dioxide sodium salt dihydrate
|
| Einecs |
204-886-1
|
| E number |
E 954
|
| Chemical formula |
C7H4NNaO3S·2H2O
|
| Relative molecular m{ass |
241,19
|
| Assay |
Not less than 99% and not more than 101% of C7H4NNaO3S·on the anhydrous basis |
| Description |
White crystals or a white crystalline efflorescent powder, odourless or with a faint odour, having an intensely sweet taste, even in very dilute solutions. Approximately between 300 and 500 times as sweet as sucrose in dilute solutions |
| Identification |
|
| Solubility |
Freely soluble in water, sparingly soluble in ethanol |
| Purity |
|
| Loss on drying |
Not more than 15% (120°C, four hours)
|
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Selenium |
Not more than 30 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Lead |
Not more than 1 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Heavy metals |
Not more than 10 mg/kg expressed as Pb on dry weight basis
|
| Benzoic and salicylic acid |
To 10 ml of a 1 in 20 solution, previously acidified with five drops of acetic acid, add three drops of an approximately molar solution of ferric chloride in water. No precipitate or violet colour appears |
| o-Toluenesulphonamide |
Not more than 10 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| P-Toluenesulphonamide |
Not more than 10 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Benzoic acid p-sulfonamide |
Not more than 25 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Readily carbonizable substances |
Absent |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 954 -- SACCHARIN AND ITS Na. K AND Ca SALTS -- contd. |
|
| (III) CALCIUM SACCHARIN |
|
| Synonyms |
Saccharin, calcium salt of saccharin |
| Definition |
|
| Chemical name |
Calcium o-benzosulphimide,
calcium salt of 2,3-dihydro-3-oxobenzisosulphonazole,
1,2-benzisothiazolin-3-one-1,1-dioxide
calcium salt hydrate (2:7)
|
| Einecs |
229-349-0
|
| E number |
E 954
|
| Chemical formula |
C14H8CaN2O6S2 3½H2O
|
| Relative molecular mass |
467,48
|
| Assay |
Not less than 95% of C14H8CaN2O6S2 on the anhydrous basis |
| Description |
White crystals or a white crystalline powder, odourless or with a faint odour, having an intensely sweet taste, even in very dilute solutions. Approximately between 300 and 500 times as sweet as sucrose in dilute solutions |
| Identification |
|
| Solubility |
Freely soluble in water, soluble in ethanol |
| Purity |
|
| Loss on drying |
Not more than 13,5% (120°C, four hours)
|
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Selenium |
Not more than 30 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Lead |
Not more than 1 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Heavy metals |
Not more than 10 mg/kg expressed as Pb on dry weight basis
|
| Benzoic and salicylic acid |
To 10 ml of a 1 in 20 solution, previously acidified with five drops of acetic acid, add three drops of an approximately molar solution of ferric chloride in water. No precipitate or violet colour appears |
| o-Toluenesulphonamide |
Not more than 10 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| P-Toluenesulphonamide |
Not more than 10 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Benzoic acid p-sulfonamide |
Not more than 25 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Readily carbonizable substances |
Absent |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 954 -- SACCHARIN AND ITS Na. K AND Ca SALTS -- contd. |
|
| (IV) POTASSIUM SACCHARIN |
|
| Synonyms |
Saccharin, potassium salt of saccharin |
| Definition |
|
| Chemical name |
Potassium o-benzosulphimide, potassium salt of- 2,3-dihydro-3-oxobenzisosulphonazole, potassium salt of 1,2-benzisothiazolin-3-one-1,1-dioxide monohydrate |
| Einecs |
|
| E number |
E 954
|
| Chemical formula |
C7H4KNO3SH2O
|
| Relative molecular mass |
239,77
|
| Assay |
Not less than 99% and not more than 101% of C7H4KNO3S2on the anhydrous basis |
| Description |
White crystals or a white crystalline powder, odourless or with a faint odour having an intensely sweet taste, even in very dilute solutions. Approximately between 300 and 500 times as sweet as sucrose |
| Identification |
|
| Solubility |
Freely soluble in water, sparingly soluble in ethanol |
| Purity |
|
| Loss on drying |
Not more than 8% (120 °C, four hours)
|
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Selenium |
Not more than 30 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Lead |
Not more than 1 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Heavy metals |
Not more than 10 mg/kg expressed as Pb on dry weight basis
|
| Benzoic and salicylic acid |
To 10 ml of a 1 in 20 solution, previously acidified with five drops of acetic acid, add three drops of an approximately molar solution of ferric chloride in water. No precipitate or violet colour appears |
| o-Toluenesulphonamide |
Not more than 10 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| P-Toluenesulphonamide |
Not more than 10 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Benzoic acid p-sulfonamide |
Not more than 25 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Readily carbonizable substances |
Absent |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 957 -- THAUMATIN |
|
| Synonyms |
|
| Definition |
|
| Chemical name |
Thaumatin is obtained by aqueous extraction (pH 2.5 to 4) of the arils of the fruit of the natural strain of Thaumatococcus daniellii (Benth) and consists essentially of the proteins thaumatin I and thaumatin II together with minor amounts of plant constituents derived from the source material |
| Einecs |
258-822-2
|
| E number |
E 957
|
| Chemical formula |
Polypeptide of 207 amino acids
|
| Relative molecular mass |
Thaumatin I 22209
Thaumatin II 22293
|
| Assay |
Not less than 16% nitrogen on the dried basis equivalent to not less than 94% proteins (N x 5,8) |
| Description |
Odourless, cream-coloured powder with an intensely sweet taste. Approximately 2 000 to 3 000 times as sweet as sucrose |
| Identification |
|
| Solubility |
Very soluble in water, insoluble in acetone |
| Purity |
|
| Loss on drying |
Not more than 9% (105 °C to constant weight)
|
| Carbohydrates |
Not more than 3% expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Sulphated ash |
Not more than 2% expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Aluminium |
Not more than 100 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Lead |
3 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Microbiological criteria |
Total aerobic microbial count: Max 1,000/g E. Coli: absent in 1g |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E959 -- NEOHESPERIDINE DIHYDROCHALCONE |
|
| Synonyms |
Neohesperidine dihydrochalcone, NHDC, hesperetin dihydrochalcone-4'-ß- neohesperidoside, neohesperidin DC |
| Definition |
|
| Chemical name |
2-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-4'-ß-D-glucopyranosyl hesperetin dihydrochalcone; obtained by catalytic hydrogenation of neohesperidin |
| Einecs |
243-978-6
|
| E number |
E 959
|
| Chemical formula |
C28H36O15
|
| Relative molecular mass |
612,6
|
| Assay |
Content not less than 96% on the dried basis |
| Description |
Off while, odourless, crystalline powder having a characteristic, intensive sweet taste. Approximately between 1 000 and 1 800 times as sweet as sucrose |
| Identification |
|
| A. Solubility |
Freely soluble in hot water, very slightly soluble in cold water, practically insoluble in ether and benzene |
| B. Ultraviolet absorption maximum |
282 to 283 nm for a solution of 2 mg in 100 ml methanol |
| C. Neu's test |
Dissolve about 10 mg of neohesperidine DC in 1 ml methanol, add 1 ml of a 1% 2-aminoethyl diphenyl borate methanolic solution. A bright yellow colour is produced |
| Purity |
|
| Loss on drying |
Not more than 11% (105°C, three hours)
|
| Sulphated ash |
Not more than 0.2% expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Lead |
Not more than 2 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis
|
| Heavy metal |
Not more than 10 mg/kg expressed as Pb on dry weight basis |
|
|
|
SCHEDULE IV
|
|
|
PART A
|
|
|
List of Permitted Food Colours
|
|
|
Note: Aluminium lakes prepared from colours mentioned in this Part are authorized
|
|
|
|
|
|
| EC Number |
Common Name |
Colour Index Number(1) or description |
| E100 |
Curcumin |
75300 |
| E101 |
(i) Riboflavin |
|
|
(ii) Riboflavin-5'-phosphate |
|
| E102 |
Tartrazine |
19140 |
| E104 |
Quinoline Yellow |
47005 |
| E110 |
Sunset Yellow FCF |
15985 |
|
Orange Yellow S |
|
| E120 |
Cochineal, Carminic acid. Carmines |
75470 |
| E122 |
Azorubine, Carmoisine |
14720 |
| E123 |
Amaranth |
16185 |
| E124 |
Ponceau 4R, Cochineal Red A |
16255 |
| E127 |
Erythrosine |
45430 |
| E128 |
Red 2G |
18050 |
| E129 |
Allura Red AC |
16035 |
| E131 |
Patent Blue V |
42051 |
| E132 |
Indigotine, Indigo carmine |
73015 |
| E133 |
Brilliant Blue FCF |
42090 |
| E140 |
Chlorophylls and |
75810 |
|
Chlorophyllins |
75815 |
|
(i) Chlorophylls |
|
|
(ii) Chlorophyllins |
|
| E141 |
Copper complexes of chlorophylls and chlorophyllins |
75815 |
|
(i) Copper complexes of chlorophylls |
|
|
(ii) Copper complexes of chlorophyllins |
|
| E 142 |
Greens S |
44090 |
| E150a |
Plain caramel (2) |
|
| E150b |
Caustic sulphite caramel |
|
| E150c |
Ammonia caramel |
|
| E150d |
Sulphite ammonia caramel |
|
| E151 |
Brilliant Black BN, Black PN |
28440 |
| E153 |
Vegetable carbon |
|
| E154 |
Brown FK |
|
| E155 |
Brown HT |
20285 |
| E160a |
Carotenes: |
|
|
(i) Mixed carotenes |
75130 |
|
(ii) Beta-carotene |
40800 |
| E160b |
Annatto, bixin, norbixin |
75120 |
| E160c |
Paprika extract, capsanthin, capsorubin |
|
| E160d |
Lycopene |
|
|
|
|
(1) Colour index numbers are taken from the third edition 1982 of the Colour Index, volumes 1 to 7, 1315. Also amendments 37 to 40 (125), 41 to 44 (127-50), 45 to 48 (130), 49 to 52 (132-50), 53 to 56 (135).
|
|
|
(2) The term caramel relates to products of a more or less intense brown colour which are intended for colouring. It does not correspond to the sugary aromatic product obtained from heating sugars and which is used for flavouring food (e.g. confectionery, pastry, alcoholic drinks).
|
|
|
|
|
|
| EC Number |
Common Name |
Colour Index Number(1) or description |
| E160e |
Beta-apo-8' carotenal (C 30) |
40820 |
| E160f |
Ethyl ester of beta-apo-8-'carotenic acid |
40825 |
|
(C30) |
|
| E161b |
Lutein |
|
| E161g |
Canthaxanthin |
|
| E162 |
Beetroot Red, betanin |
|
| E163 |
Anthocyanins |
Prepared by physical means from fruits and vegetables
|
| E170 |
Calcium carbonate |
77220 |
| E171 |
Titanium dioxide |
77891 |
| E172 |
Iron oxides and hydroxides |
77491 |
|
|
77492 |
|
|
77499 |
| E173 |
Aluminium |
|
| E174 |
Silver |
|
| E175 |
Gold |
|
| E180 |
Litholrubine BK |
|
|
|
|
(1) Colour index numbers are taken from the third edition 1982 of the Colour Index, volumes 1 to 7, 1315. Also amendments 37 to 40 (125), 41 to 44 (127-50), 45 to 48 (130), 49 to 52 (132-50), 53 to 56 (135).
|
|
|
PART B
|
|
|
Foodstuffs which may not Contain Added Colours, Except Where Specifically Provided for in Parts, C, D or E
|
|
|
(The designations used in Part B do not prejudice the "carry over'' principle in cases where products contain ingredients with legitimate colouring in their own right).
|
|
|
1. Unprocessed foodstuffs
|
|
|
2. All bottled or packed waters
|
|
|
3. Milk, semi-skimmed and skimmed milk, pasteurised or sterilised (including UHT sterilisation) (unflavoured)
|
|
|
4. Chocolate milk
|
|
|
5. Fermented milk (unflavoured)
|
|
|
6. Preserved milks as mentioned in Directive 76/118/EEC
|
|
|
7. Butter-milk (unflavoured)
|
|
|
8. Cream and cream powder (unflavoured)
|
|
|
9. Oils and fats of animal or vegetable origin
|
|
|
10. Eggs and egg products as defined in Article 2 (1) of Directive 89/437/EEC
|
|
|
11. Flour and other milled products and starches
|
|
|
12. Bread and similar products
|
|
|
13. Pasta and gnocchi
|
|
|
14. Sugar, including all mono- and disaccharides
|
|
|
15. Tomato paste and canned and bottled tomatoes
|
|
|
16. Tomato-based sauces
|
|
|
17. Fruit juice and fruit nectar as mentioned in Directive 75/726/EEC and vegetable juice
|
|
|
18. Fruit, vegetables (including potatoes) and mushrooms -- canned, bottled or dried; processed fruit, vegetables (including potatoes) and mushrooms)
|
|
|
19. Extra jam, extra jelly, and chestnut puree as mentioned in Directive 79/693/EEC, creme de pruneaux
|
|
|
20. Fish, molluscs and crustaceans, meat, poultry and game as well as their preparations, but not including prepared meals containing these ingredients.
|
|
|
21. Cocoa products and chocolate components in chocolate products as mentioned in Directive 73/241/EEC
|
|
|
22. Roasted coffee, tea, chicory, tea and chicory extracts; tea, plant, fruit and cereal preparations for infusions, as well as mixes and instant mixes of these products
|
|
|
23. Salt, salt substitutes, spices and mixtures of spices
|
|
|
24. Wine and other products defined by Regulation (EEC) No. 822/87
|
|
|
25. Korn, Kornbrand, fruit spirit drinks, Fruit Spirits, Ouzo, Grappa, Tsikoudia from Crete, Tsipouro from Macedonia, Tsipouro from Thessaly, Tsipouro from Tyrnavos, Eau de vie de marc Marque nationale luxembourgeoise, Eau de vie de seigle Marque nationale luxembourgeoise, London gin, as defined in Regulation (EEC) No. 1576/89
|
|
|
26. Sambuca, Maraschino and Mistra as defined in Regulation (EEC) No. 1180/91
|
|
|
27. Sangria, Clarea and Zurra as mentioned in Regulation (EEC) No. 1601/91
|
|
|
28. Wine vinegar
|
|
|
29. Foods for infants and young children as mentioned in Directive 89/398/EEC including foods for infants and young children not in good health
|
|
|
30. Honey
|
|
|
31. Malt and malt products
|
|
|
32. Ripened and unripened cheese (unflavoured)
|
|
|
33. Butter from sheep and goats' milk
|
|
|
PART C
|
|
|
Foodstuffs to Which Only Certain Permitted Colours May be Added
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Foodstuffs |
Permitted colour |
Maximum level |
|
Malt Bread
|
E 150a Plain caramel
|
quantum satis |
|
|
E 150b Caustic sulphite caramel
|
|
|
|
E 150c Ammonia caramel
|
|
|
|
E 150d Sulphite ammonia caramel
|
|
|
Beer
|
E 150a Plain caramel
|
quantum satis |
|
Cider bouché
|
E 150b Caustic sulphite caramel
|
|
|
|
E 150c Ammonia caramel
|
|
|
|
E 150d Sulphite ammonia caramel
|
|
| Butter (including reduced fat butter and concentrated butter) |
E 160a Carotenes
|
quantum satis |
| Margarine, minarine, other fat emulsions, and fats essentially free from water |
E 160a Carotenes
|
quantum satis |
|
|
E 100 Curcumin
|
quantum satis |
|
|
E 160b Annatto, Bixine,
|
10 mg/kg |
|
|
Norbixine
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Foodstuffs |
Permitted colour |
Maximum level |
|
Sage Derby cheese
|
E 140 Chlorophylls
|
quantum satis |
|
|
Chlorophyllins
|
|
|
|
E 141 Copper complexes of chlorophylls and chlorohyllins
|
|
| Ripened Orange, Yellow and broken- white cheese; unflavoured processed cheese |
E 160a Carotenes
E 160c Paprika extract
|
quantum satis |
|
E 160b Annatto, Bixin, Norbixin
|
15 mg/kg |
|
|
|
|
Red Leicester cheese
|
E 160b Annatto, Bixin, Norbixin
|
50 mg/kg |
|
Mimolette cheese
|
E 160b Annatto, Bixin, Norbixin
|
35 mg/kg |
|
Morbier cheese
|
E 153 Vegetable carbon
|
quantum satis |
|
Red marbled cheese
|
E 120 Cochineal, Carminic acid.
Carmines
|
125 mg/kg |
|
|
E 163 Anthocyanins
|
quantum satis |
|
Vinegar
|
E 150a Plain caramel
|
quantum satis |
|
|
E 150b Caustic sulphite caramel
|
|
|
|
E 150c Ammonia caramel
|
|
|
|
E 150d Sulphite ammonia caramel
|
|
| Whisky, Whiskey, grain spirit (other than Korn or Kornbrand or Eau de vie de seigle Marque nationale luxembourgeoise), wine spirit, rum. Brandy, Weinbrand, grape marc, grape marc spirit (other than Tsikoudia and Tsipouro and Eau de vie de marc Marque nationale luxembourgeoise), Grappa invecchiata, Bagaceira velha as mentioned in Regulation (EEC) No. 1576/89 |
E 150a Plain caramel
E 150b Caustic sulphite caramel
E 150c Ammonia caramel
E 150d Sulphite ammonia caramel
|
quantum satis |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Foodstuffs |
Permitted colour |
Maximum level |
| Aromatized wine-based drinks (except bitter soda) and aromatized wines as mentioned in Regulation (EEC) No. 1601/91 |
E 150a Plain caramel
E 150b Caustic sulphite caramel
E 150c Ammonia caramel
E 150d Sulphite ammonia caramel
|
quantum satis |
| Americano |
E 150a Plain caramel
|
quantum satis |
|
E 150b Caustic sulphite caramel
|
|
|
E 150c Ammonia caramel
|
|
|
E 150d Sulphite ammonia caramel
|
|
|
E 163 Anthocyanins
|
|
|
E 100 Curcumin
E 101 (i) Riboflavin
(ii) Riboflavin-5'- phosphate
|
100 mg/l (individually or in combination) |
|
E 102 Tartrazine
|
|
|
E 104 Quinoline Yellow
|
|
|
E 120 Cochineal, Carminic acid, Carmines
|
|
|
E 122 Azorubine carmoisine
|
|
|
E 123 Amaranth
|
|
|
E 124 Ponceau 4R
|
|
| Bitter soda, bitter vino as mentioned in Regulation (EEC) No. 1601/91 |
E 150a Plain caramel
|
quantum satis |
|
E 150b Caustic sulphite caramel
|
|
|
E 150c Ammonia caramel
|
|
|
E 150d Sulphite ammonia caramel
|
|
|
E 100 Curcumin |
100 mg/l (individually or in combination) |
|
E 101 (i) Riboflavin
(ii) Riboflavin-5'- phosphate
|
|
|
E 102 Tartrazine
|
|
|
E 104 Quinoline Yellow
|
|
|
E 110 Sunset Yellow FCF Orange Yellow S
|
|
|
E 120 Cochineal, Carminic acid, Carmines
|
|
|
E 122 Azorubine, Carmoisine
|
|
|
E 123 Amaranth
|
|
|
E 124 Ponceau 4R, Cochineal Red A
|
|
|
E 129 Allura Red AC
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Foodstuffs |
Permitted colour |
Maximum level |
| Liqueur wines and quality liqueur wines produced in specified regions |
E 150a Plain caramel
|
quantum satis |
|
|
E 150b Caustic sulphite caramel
|
|
|
|
E 150c Ammonia caramel
|
|
|
|
E 150d Sulphite ammonia caramel
|
|
| Vegetables in vinegar, brine or oil (excluding olives) |
E 101 (i) Riboflavin
(ii) Riboflavin-5'- phosphate
|
quantum satis |
|
E 140 Chlorophylls, Chlorophyllins
|
|
|
E 150a Plain caramel
|
|
|
E 150b Caustic sulphite caramel
|
|
|
E 150c Ammonia caramel
|
|
|
E 150d Sulphite ammonia caramel
|
|
|
E 141 Copper complexes of chlorophylls and chlorophyllins
|
|
|
E 160a Carotenes: |
|
|
(i) Mixed carotenes
|
|
|
(ii) Beta-carotene
|
|
|
E 162 Beetroot Red, betanin
|
|
|
E 163 Anthocyanins
|
|
| Extruded, puffed and/or fruit-flavoured breakfast cereals |
E 150c Ammonia caramel
|
quantum satis |
|
|
E 160a Carotenes
|
quantum satis |
|
|
E 160b Annatto, Bixin, Norbixin
|
25 mg/kg |
|
|
E 160c Paprika extract, Capsanthin, Capsorubin
|
quantum satis |
| Fruit-flavoured breakfast cereals |
E 120 Cochineal, Carminic acid, Carmines
|
200 mg/kg in |
|
|
E 162 Beetroot Red, betanine
|
(individually or |
|
|
E 163 Anthocyanins
|
combination) |
| Jam, jellies and marmalades as mentioned in Directive 79/693/EEC and other similar fruit preparations including low calorie products |
E 100 Curcumin
|
quantum satis |
|
|
E 140 Chlorophylls and chlorophyllins
|
|
|
E 141 Copper complexes of chlorophylls and chlorophyllins
|
|
|
E 150a Plain caramel
|
|
|
E 150b Caustic sulphite caramel
|
|
|
E 150c Ammonia caramel
|
|
|
E 150d Sulphite ammonia caramel
|
|
|
E 160a Carotenes:
|
|
|
(i) Mixed carotenes
|
|
|
(ii) Beta-carotene
|
|
|
E 160c Paprika extract, Capsanthin, Capsorubin
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Foodstuffs |
Permitted colour |
Maximum level |
|
E 162 Beetroot Red, betanin
|
|
|
E 163 Anthocyanins
|
|
|
E 104 Quinoline Yellow
|
100 mg/kg (individually or in combination) |
|
E 110 Sunset Yellow
|
|
|
E 120 Cochineal, Carminic acid, Carmines
|
|
|
E 124 Ponceau 4R, Cochineal
|
|
|
E 142 Green S
|
|
|
E 160d Lycopene
|
|
|
E 161b Lutein
|
|
|
Sausages, pâtés and terrines
|
E 100 Curcumin
|
20 mg/kg |
|
E 120 Cochineal, Carminic acid, Carmines
|
100 mg/kg |
|
E 150a Plain caramel
|
quantum satis |
|
E 150b Caustic sulphite caramel
|
quantum satis |
|
E 150c Ammonia caramel
|
quantum satis |
|
E 150d Sulphite ammonia caramel
|
quantum satis |
|
E 160a Carotenes
|
|
|
E 160c Paprika extract, Capsanthin, Capsorubin
|
20 mg/kg
10 mg/kg
|
|
E 162 Beetroot Red, betanin
|
quantum satis |
| Luncheon meat |
E 129 Allura Red
|
25 mg/kg |
| Breakfast sausages with a minimum cereal content of 6% |
E 129 Allura Red AC
|
25 mg/kg |
| Burger meat with a minimum vegetable and/or cereal content of 4% |
E 120 Cochineal, Carminic acid. Carmines
|
100 mg/kg |
|
E 150a Plain caramel
|
quantum satis |
|
E 150b Caustic sulphite caramel
|
quantum satis |
|
E 150c Ammonia caramel
|
quantum satis |
|
E 150d Sulphite ammonia caramel
|
quantum satis |
| Chorizo sausage |
E 120 Cochineal Carminic acid, Carmines
|
200 mg/kg |
| Salchichon |
E 124 Ponceau 4R, Cochineal Red A
|
250 mg/kg |
| Sobrasada |
E 110 Sunset Yellow FCF
|
135 mg/kg |
|
E 124 Ponceau 4R, Cochineal Red A
|
200 mg/kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Foodstuffs |
Permitted colour |
Maximum level |
| Pasturmas (edible external coating) |
E 100 Curcumin |
quantum satis |
|
E 101 (i) Riboflavin
|
|
|
(ii) Riboflavin-5'-phospate
|
|
|
E 120 Cochineal, Carminic acid, Carmines
|
|
| Dried potato granules and flakes |
E 100 Curcumin
|
quantum satis |
| Processed mushy and garden peas (canned) |
E 102 Tartrazine
|
100mg/kg |
|
E 133 Brilliant Blue
|
20mg/kg |
|
E 142 Green S
|
10mg/kg |
|
|
|
PART D
|
|
|
Colours Permitted for Certain Uses Only
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Colour |
Foodstuff |
Maximum level |
| E 123 Amaranth |
Aperitif wines, spirit drinks including products with less than 15% alcohol by volume
|
30mg/l |
|
Fish roe
|
30 mg/kg |
| E 127 Erythrosine |
Cocktail cherries and candied cherries
|
200 mg/kg |
|
Bigarreaux cherries in syrup and in cocktails
|
150 mg/kg |
| E 128 Red 2G |
Breakfast sausages with a minimum cereal content of 6%
Burger meat with a minimum vegetable and/or cereal content of 4%
|
20 mg/kg |
| E 154 Brown FK |
Kippers
|
20 mg/kg |
| E 161g Canthaxanthin |
Saucisses de Strasbourg
|
15 mg/kg |
| E 173 Aluminium |
External coating of sugar confectionery for the decoration of cakes and pastries
|
quantum satis |
| E 174 Silver |
External coating of confectionery Decoration of chocolates Liqueurs
|
quantum satis |
| E 175 Gold |
External coating of confectionery
|
quantum satis |
|
Decoration of chocolates
|
|
|
Liqueurs
|
|
| E 180 Litholrubine BK |
Edible cheese rind |
quantum satis |
| E 160b Annatto, Bixin, Norbixin |
Margarine, Minarine other fat emulsions, and fats essentially free from water
|
10 mg/kg |
|
Decorations and coatings
|
20mg/kg |
|
Fine bakery wares
|
10mg/kg |
|
Edible ices
|
20mg/kg |
|
Liqueurs, including fortified beverages with less than 15% alcohol by volume
|
10mg/l |
|
Flavoured processed cheese
|
15mg/kg |
|
Ripened Orange, Yellow and broken-white cheese
|
15mg/kg |
|
Unflavoured processed cheese
|
15 mg/kg |
|
Desserts |
10 mg/kg |
|
Snacks: dry, savoury potato, cereal or starch-based snack products:
|
|
|
--Extruded or expanded savoury snack products
|
20 mg/kg |
|
--Other savoury snack products and savoury coated nuts
|
10 mg/kg |
|
Smoked fish
|
10 mg/kg |
|
Edible cheese rind and edible casings
|
20 mg/kg |
|
Red Leicester cheese
|
50 mg/kg |
|
Mimolette cheese
|
35 mg/kg |
|
Extruded, puffed and/or fruit-flavoured breakfast cereals
|
25 mg/kg |
|
|
|
PART E
|
|
|
Colours Permitted in Foodstuffs Other Than Those Mentioned in Parts B and C
|
|
|
SECTION 1
|
|
|
The following colours may be used in foodstuffs mentioned in Part E Section 2 and in all other foodstuffs other than those listed in Parts B and C at quantum satis.
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 101 |
(i) Riboflavin |
|
(ii) Riboflavin-5'- phosphate |
| E 140 |
Chlorophylls and chlorophyllins |
| E 141 |
Copper complexes of chlorophylls and chlorophyllins |
| E 150a |
Plain caramel |
| E 150b |
Caustic sulphite caramel |
| E 150c |
Ammonia caramel |
| E 150d |
Sulphite ammonia caramel |
| E 153 |
Vegetable carbon |
| E 160a |
Carotenes |
| E 160c |
Paprika extract, capsanthin, capsorubin |
| E 162 |
Beetroot Red, betanin |
| E 163 |
Anthocyanins |
| E 170 |
Calcium carbonate |
| E 171 |
Titanium dioxide |
| E 172 |
Iron oxides and hydroxides |
|
|
|
SECTION 2
|
|
|
The following colours may be used singly or in combination in the following foods up to the maximum level specified in the table. However, for non-alcoholic flavoured drinks, edible ices, desserts, fine bakery wares and confectionery, colours may be used up to the limit indicated in the appropriate table but the quantities of each of the colours E 110, E 122, E 124 and E 155 may not exceed 50 mg/kg or mg/1.
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 100 |
Curcumin |
| E 102 |
Tartrazine |
| E 104 |
Quinoline Yellow |
| E 110 |
Sunset Yellow FCF
Orange Yellow S
|
| E 120 |
Cochineal, Carminic acid. Carmines |
| E 122 |
Azorubine, Carmoisine |
| E 124 |
Ponceau 4R, Cochineal Red A |
| E 129 |
Allura Red AC |
| E 131 |
Patent Blue V |
| E 132 |
Indigotine, Indigo carmine |
| E 133 |
Brilliant Blue FCF |
| E 142 |
Green S |
| E 151 |
Brilliant Black BN, Black PN |
| E 155 |
Brown HT |
| E 160d |
Lycopene |
| E 160e |
Beta-apo-8' carotenal (C 30) |
| E 160f |
Ethyl ester of beta-apo-8'-carotenic acid (C 30) |
| E 161b |
Lutein |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Foodstuffs |
Maximum Level |
|
Non-alcoholic flavoured drinks
|
100 mg/l |
|
Candied fruits and vegetables, Mostarda di frutta
|
200 mg/kg |
|
Preserves of red fruits
|
200 mg/kg |
|
Confectionery
|
300 mg/kg |
|
Decorations and coatings
|
500 mg/kg |
|
Fine bakery wares (e.g. viennoiserie, biscuits, cakes and wafers)
|
200 mg/kg |
|
Edible ices
|
150 mg/kg |
|
Flavoured processed cheese
|
150 mg/kg |
| Desserts including flavoured milk products |
100 mg/kg |
| Sauces, seasonings (for example, curry powder, tandoori), pickles, relishes, chutney and piccalilli |
500 mg/kg |
|
Mustard
|
300 mg/kg |
|
Fish paste and crustacean paste
|
100 mg/kg |
|
Pre-cooked crustaceans
|
250 mg/kg |
|
Salmon substitutes
|
500 mg/kg |
|
Surimi
|
500 mg/kg |
|
Fish roe
|
300 mg/kg |
|
Smoked fish
|
100 mg/kg |
| 'Snacks': dry, savoury potato, cereal or starch-based snack products: |
|
|
--Extruded or expanded savoury snack products
|
200 mg/kg |
|
--Other savoury snack products and savoury coated nuts
|
100 mg/kg |
|
Edible cheese rind and edible casings
|
quantum satis |
| Complete formulae for weight control intended to replace total daily food intake or an individual meal |
50 mg/kg
|
| Complete formulae and nutritional supplements for use under medical supervision |
50 mg/kg
|
|
Liquid food supplements/dietary integrators
|
100 mg/l |
|
Solid food supplements/dietary integrators
|
300 mg/kg |
|
Soups
|
50 mg/kg
|
|
Meat and fish analogues based on vegetable proteins
|
100 mg/kg |
| Spirituous beverages (including products less than 15% alcohol by volume), except those mentioned in Part B and C |
200 mg/l
|
| Aromatised wines, aromatised wine-based drinks and aromatised wine-product cocktails as mentioned in Regulation (EEC) No. 1601/91, except those mentioned on Parts B and C |
200 mg/l
|
| Fruit wines (still or sparkling) cider (except cider bouche) and perry aromatised fruit wines, cider and perry |
200 mg/l
|
|
|
|
SCHEDULE V
|
|
|
Specific Purity Criteria concerning Colours for use in Foodstuffs
|
|
|
A. GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS FOR ALUMINIUM LAKES OF COLOURS
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Definition |
Aluminium lakes are prepared by reacting colours complying with the purity criteria set out in the appropriate specification monograph with alumina under aqueous conditions. The alumina is usually freshly prepared undried material made by reacting aluminium sulfate or chloride with sodium or calcium carbonate or bicarbonate of ammonia. Following lake formation, the product is filtered, washed with water and dried. Unreacted alumina may also be present in the finished product. |
|
HCI insoluble matter
|
Not more than 0,5%
|
|
Ether extractable matter
|
Not more than 0,2% (under neutral conditions)
Specific purity criteria for the corresponding colours are applicable.
|
|
|
|
B. SPECIFIC CRITERIA OF PURITY
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 100 CURCUMIN |
|
| Synonyms |
CI Natural Yellow 3, Turmeric Yellow, Diferoyl Methane
|
| Definition |
Curcumin is obtained by solvent extraction of turmeric i.e. the ground rhizones of natural strains of Curcuma longa L. In order to obtain a concentrated curcumin powder, the extract is purified by crystallisation. The product consists essentially of curcumins; i.e. the colouring principle (l,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl) hepta-1,6-dien-3,5-dione) and its two desmethoxy derivatives in varying proportions. Minor amounts of oils and resins naturally occurring in turmeric may be present.
Only the following solvents may be used in the extraction: ethylacetate, acetone, carbon dioxide, dichloromethane, n-butanol, methanol, ethanol, hexane.
|
|
Class
|
Dicinnamoylmethane |
|
Colour Index No.
|
75300 |
|
Einics
|
207-280-5 |
|
Chemical names
|
I 1,7-Bis (4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl) hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione
|
|
|
II 1-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)-7-(4-hyaroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl-) hepta-l,6-diene-3,5-dione
|
|
|
III 1,7-Bis(4-hydroxyphenyl) hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione
|
|
Chemical formula
|
I C21H20O6
|
|
|
II C20H18O5
|
|
|
III C19H16O4
|
|
Molecular weight
|
I.368,39 II. 338,39 III. 308,39 |
|
Assay
|
Content not less than 90% total colouring matters
 1 607 at ca 426 nm in ethanol 1 607 at ca 426 nm in ethanol
|
| Description |
Orange-yellow crystalline powder |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Identification |
|
|
A. Spectrometry
|
Maximum in ethanol at ca 426 nm |
|
B. Melting Range
|
179-182 °C |
| Purity |
Ethylacetate |
 |
Not more than 50 mg/kg, singly or in combination |
|
Solvent residues
|
Acetone |
|
n-butanol |
|
Methanol |
|
Ethanol |
|
Hexane |
|
Dichloromethane: not more than 10 mg/kg |
|
Arsenic
|
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
|
Lead
|
Not more than 10 mg/kg |
|
Mercury
|
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Cadmium |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
|
Heavy Metals (as Pb)
|
Not more than 40 mg/kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 101 (i) RIBOFLAVIN |
|
| Synonyms |
Lactoflavin |
|
Class
|
Isoalloxazine |
|
Einecs
|
201--507-1 |
|
Chemical names
|
7, 8--Dimethyl-10-(D-ribo-2, 3, 4, 5-tetrahydroxypentyl) benzo(g)--pteridine-2, 4-(3H, 10H)-dione |
|
|
7,8--dimethyl-10 (1'-D-ribityl) isoalloxazine |
|
Chemical formula
|
C17H20N4O6 |
|
Molecular weight
|
376,37 |
|
Assay
|
Content not less than 98% on the anhydrous basis  328 at ca 444 nm in aqueous solution 328 at ca 444 nm in aqueous solution
|
| Description |
Yellow to orange-yellow crystalline powder, with slight odour. |
| Identification |
|
|
A. Spectrometry
|
The ratio A375/A267 is between 0,31 and 0,33
The ratio A444/A267 is between 0,36 and 0,39
|
 In aqueous solution In aqueous solution
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Maximum in water at ca 375 nm. |
|
B. Specific rotation
|
(α) 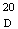 between -115° and -140° in a 0,05 N sodium hydroxide solution between -115° and -140° in a 0,05 N sodium hydroxide solution
|
| Purity |
|
|
Loss on drying
|
Not more than 1,5% after drying at 105°C for 4 hrs |
|
Sulfated ash
|
Not more than 0,1% |
|
Primary aromatic amines
|
Not more than 100 mg/kg (calculated as aniline) |
|
Arsenic
|
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
|
Lead
|
Not more than 10 mg/Kg |
|
Mercury
|
Not more than 10mg/kg |
|
Cadmium
|
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
|
Heavy metals (as Pb)
|
Not more than 40 mg/kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 101 (ii) (ii) RIBOFLAVIN-5'-PHOSPHATE |
|
| Synonyms |
Riboflavin-5'-phosphate sodium |
| Definition |
These specifications apply to riboflavin -5--'phosphate together with minor amounts of free riboflavin diphosphate |
|
Class
|
Isoalloxazine |
|
Einics
|
204--988-6 |
|
Chemical names
|
Monosodium |
|
|
(2R, 3R, 4S)--5--(3) 10'-dihydro-7, 8'-dimethyl-2', 4'-dioxo-10-'benzo [y]pteridinyl]-2, 3, 4- |
|
|
trihydroxypentyl phosphate; monosodium salt of 5'-monophosphate ester of riboflavin |
|
Chemical formula
|
For the dihydrate form: C17H20N4NaO9P.2H2O |
|
For the anhydrous form: C17H20N4NaO9P |
|
Molecular weight
|
541,36 |
|
Assay
|
Content not less than 95% total colouring matters calculated as C17H20N4NaO9P.2H2O
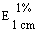 250 at ca 375 nm in aqueous solution 250 at ca 375 nm in aqueous solution
|
| Description |
Yellow to orange crystalline hygroscopic powder, with slight odour and a bitter taste |
| Identification |
|
|
A. Spectrometry
|
The ratio A375/A267 is between 0,30 and 0,34
The ratio A444/A267 is between 0,35 and 0,40
|
 In aqueous solution In aqueous solution
|
|
|
Maximum in water at ca 375 nm. |
|
B. Specific rotation
|
(α) 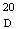 between +38° and +42° in a 5 molar HCI solution between +38° and +42° in a 5 molar HCI solution
|
| Purity |
|
|
Loss on drying
|
Not more than 8% (100°C, 5 hrs in vacuum over P2O5) for the dihydrate form |
|
Sulfated ash
|
Not more than 25% |
|
Inorganic phosphate
|
Not more than 1,0% (calculated as PO4 on the anhydrous basis) |
|
Subsidiary colouring matters
|
Riboflavin (free): Not more than 6% |
|
|
Riboflavin diphosphate: Not more than 6% |
|
Primary aromatic amines
|
Not more than 70 mg/kg (calculated as aniline) |
|
Arsenic
|
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
|
Lead
|
Not more than 10 mg/kg |
| Mercury |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
|
Cadmium
|
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
|
Heavy metals (as Pb)
|
Not more than 40 mg/kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 102 TARTRAZINE |
|
| Synonyms |
CI Food Yellow 4 |
| Definition |
Tartrazine consists essentially of trisodium 5--hydroxy-l-(4-sulfonatophenyl)--4-(4-sulfonatophenylazo-H-pyrazole-30-carboxylate and subsidiary colouring matters together with sodium chloride and/or sodium sulfate as the principal uncoloured components Tartrazine is described as the sodium salt The calcium and the potassium salt are also permitted |
|
Class
|
Monoazo |
|
Colour Index No
|
19140 |
|
Einics
|
217--699-5 |
|
Chemical names
|
Trisodium-5--hydroxy-l-(4-sulfonatophenyl)--4-(4-sulfonatophenylazo)-H-pyrazole-3-carboxylate |
|
Chemical formula
|
C16H9N4 Na3O9S2 |
|
Molecular weight
|
534,37 |
|
Assay
|
Content not less than 85% total colouring matters calculated as the sodium salt 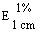 530 at ca 426 nm in aqueous solution 530 at ca 426 nm in aqueous solution
|
| Description |
Light orange powder or granules |
| Identification |
|
|
A. Spectrometry
|
Maximum in water at ca 426 nm |
|
B. Yellow solution in water
|
|
| Purity |
|
|
Water insoluble matter
|
Not more than 0,2% |
|
Subsidiary colouring matters
|
Not more than 1,0% |
|
Organic compounds other than colouring matters:
|
|
| 4--hydrazinobenzene sulfonic acid |
 |
Total not more than 0,5%
|
|
4--aminobenzene-1-sulfonic acid
|
|
5--oxo-1-(4-sulfophenyl)--2-pyrazolin-e-3-carboxylic acid
|
|
4, 4'-diazoaminodi (benzene sulfonic acid)
|
|
Tetrahydroxysuccinic acid
|
|
Unsulfonated primary aromatic amines
|
Not more than 0,01% (calculated as aniline) |
|
Ether extractable matter
|
Not more than 0,2% under neutral conditions |
|
Arsenic
|
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
|
Lead
|
Not more than 10 mg/kg |
|
Mercury
|
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
|
Cadmium
|
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
|
Heavy metals (as Pb)
|
Not more than 40 mg/kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 104 QUINOLINE YELLOW |
|
| Synonyms |
CI Food Yellow 13 |
| Definition |
Quinoline Yellow is prepared by sulfonating 2--(2-quinolyl) indan-1, 3-dione. Quinoline Yellow consists essentially of sodium salts of a mixture of disulfonates (principally), monosulfonates and trisulfonates of the above compound and subsidiary colouring matters together with sodium chloride and/or sodium sulfate as the principal uncoloured components. Quinoline Yellow is described as the sodium salt. The calcium and the potassium salt are also permitted.
|
|
Class
|
Quinophthalone |
|
Colour Index No
|
47005 |
|
Einecs
|
305--897-5 |
|
Chemical name
|
The disodium salts of the disulfonates of 2--(2-quinolyl) indan-1,3-dione (principal component) |
|
Chemical formula
|
C18H9N Na2O8S2(principal component) |
|
Molecular weight
|
477,38 (principal component) |
|
Assay
|
Content not less than 70% total colouring matters calculated as the sodium salt Quinoline Yellow shall have the following composition: |
|
Of the total colouring matters present: |
|
--not less than 80% shall be disodium 2--(2-quinolyl:) indan-1, 3-dione-disulfonates
|
|
--not more than 15% shall be sodium 2--(2-quinolyl) indan-1, 3-dione-monosulfonates
|
|
--not more than 7.0% shall be trisodium 2--(2-quinolyl) indan-1, 3-dione-trisulfonate
|
|
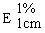 865 (principal component) at ca 411 nm in aqueous acetic acid solution 865 (principal component) at ca 411 nm in aqueous acetic acid solution
|
| Description |
Yellow powder or granules |
| Identification |
|
|
A. Spectrometry
|
Maximum in aqueous acetic acid solution of pH 5 at ca 411 nm |
|
B. Yellow solution in water
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 104 QUINOLINE YELLOW--contd. |
|
| Purity |
|
|
Water insoluble matter
|
Not more than 0.2% |
|
Subsidiary colouring matters
|
Not more than 4.0% |
|
Organic compounds other than colour matters
|
|
|
2-metyhylquinoline-sulfonic acid
|
 |
Total not more than 0,5% |
|
Phthalic acid
|
|
2,-6-dimethyl quinoline
|
|
2, 6-dimethyl quinoline sulfonic acid
|
|
2-(2-quinolyl) indan-1,3 dione
|
Not more than 4 mg/kg |
|
Unsulfonated primary aromatic amines
|
Not more than 0,01% (calculated as aniline) |
|
Ether extractable matter
|
Not more than 0,2% under neutral conditions |
|
Arsenic
|
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
|
Lead
|
Not more than 10 mg/Kg |
|
Mercury
|
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
|
Cadmium
|
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
|
Heavy metals (as Pb)
|
Not more than 40 mg/kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 110 SUNSET YELLOW FCF |
|
| Synonyms |
CI Food Yellow 3, Orange Yellow S |
| Definition |
Sunset Yellow FCF consists essentially of disodium 2--hydroxy-l-(4-sulfonatophenylazo) naphthalene-6-sulfonate and subsidiary colouring matters together with sodium chloride and/or sodium sulfate as the principal uncoloured components.
Sunset Yellow FCF is described as the sodium salt. The calcium and the potassium salt are also permitted
|
|
Class
|
Monoazo |
|
Colour Index No
|
15985 |
|
Einics
|
220--491-7 |
|
Chemical names
|
Disodium 2--hydroxy-l-(4-sulfonatophenylazo) naphthalene-6-sulfonate |
|
Chemical formula
|
C16H10N2Na2O7S2 |
|
Molecular weight
|
452,37 |
|
Assay
|
Content not less than 85% total colouring matters calculated as the sodium salt 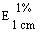 555 at ca 485 nm in aqueous solution at pH7 555 at ca 485 nm in aqueous solution at pH7
|
| Description |
Orange-red powder or granules |
| Identification |
|
|
A. Spectrometry
|
Maximum in water at ca 485 nm at pH7 |
|
B. Orange solution in water
|
|
| Purity |
|
|
Water insoluble matter
|
Not more than 0,2% |
|
Subsidiary colouring matters:
|
Not more than 5,0% |
|
Organic compounds other than colouring matters
|
|
|
4-[aminobenzene-1-sulfonic acid
|
 |
Total not more than 0,5% |
|
3-hydroxymaphthalene-2,7-disulfonic acid
|
|
6-hydroxymaphthalene-2-sulfonic acid
|
|
7-hydroxymaphthalene-1, 3-disulfonic acid
|
|
4, 4'-diazoaminodi (benzene sulfonic acid)
|
|
6,6'-oxydi(naphthalene-2-sulfonic acid)
|
|
Unsulfonated primary aromatic amines
|
Not more than 0,01% (calculated as aniline) |
|
Ether extractable matter
|
Not more than 0,2% under neutral conditions |
|
Arsenic
|
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
|
Lead
|
Not more than 10 mg/kg |
|
Mercury
|
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
|
Cadmium
|
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
|
Heavy metals (as Pb)
|
Not more than 40 mg/kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E120 COCHINEAL, CARMINIC ACID, |
|
| CARMINES |
|
| Definition |
Carmines and carminic acid are obtained from aqueous, aqueous alcoholic or alcoholic extracts from Cochineal, which consists of the dried bodies of the female insect Dactylopius coccus Costa
|
|
The colouring principle is carminic acid
|
|
Aluminium lakes of carminic acid (carmines) can be formed in which aluminium and carminic acid are thought to be present in the molar ratio 1:2
|
|
In commercial products the colouring principle is present in association with ammonium, calcium, potassium or sodium cations, singly or in combination, and these cations may also be present in excess
|
|
Commercial products may also contain proteinaceous material derived from the source insect, and may also contain free carminate or a small residue of unbound aluminium cations
|
|
Class
|
Anthraquinone |
|
Colour index No
|
75470 |
|
Einecs
|
Cochineal: 215-680-6; carminic acid: 215-023-3; carmines: 215-724-4 |
|
Chemical names
|
7-β-D-glucopyranosyl-3,5,6,8-tetrahydroxy-1-methyl-9,10-dioxoanthracene-2-carboxylicacid (carminic acid); |
|
Chemical formula
|
Carmine is the hydrated aluminum chelate of this acid C22H20O13 (carminic add) |
|
Molecular weight
|
492,39(carminic acid) |
|
Assay
|
Content not less than 2,0% carminic acid in the extracts containing carminic acid; not less than 50% carminic acid in the chelates
|
| Description |
Red to dark red, friable, solid or powder Cochineal extract is generally a dark read liquid but can also be dried as a powder
|
| Identification |
|
|
Spectrometry
|
Maximum in aqueous ammonia solution at ca 518 nm. |
|
Maximum in dilute hydrochloric solution at ca 494 nm for carminic acid |
| Purity |
|
|
Arsenic
|
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
|
Lead
|
Not more than 10 mg/Kg |
|
Mercury
|
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
|
Cadmium
|
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
|
Heavy metals (as Pb)
|
Not more than 40 mg/kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 122 AZORUBINE, CARMOISINE |
|
| Synonyms |
CI Food Red 3 |
| Definition |
Azorubine consists essentially of disodium 4--hydroxy-3-(4-sulfonato-1-naphthylazo) naphthalene -1-sulfonate and subsidiary colouring matters together with sodium chloride and/or sodium sulfate as the principal uncoloured components
|
|
Azorubine is described as the sodium salt. The calcium and the potassium salt are also permitted
|
|
Class
|
Monoazo |
|
Colour Index No
|
14720 |
|
Einecs
|
222-657-4 |
|
Chemical name
|
Disodium 4-hydroxy-3-(4-sulfonato-1-naphthylazo) naphthalene-1-sulfonate |
|
Chemical formula
|
C20H12N2Na2O7S2 |
|
Molecular weight
|
502,44 |
|
Assay
|
Content not less than 85% total colouring matters, calculated as the sodium salt 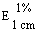 510 at ca 516 nm in aqueous solution 510 at ca 516 nm in aqueous solution
|
| Description |
Red to maroon powder or granules |
| Identification |
|
|
A. Spectrometry
|
Maximum in water at ca 516 nm |
|
B. Red solution in water
|
|
| Purity |
|
|
Water insoluble matter
|
Not more than 0,2% |
|
Subsidiary colouring matters
|
Not more than 2,0% |
|
Organic compounds other than colouring matters:
|
|
|
4--aminonaphthalene-l-sulfonic acid
|
 |
Total not more than 0,5% |
|
4--hydroxynaphthalene-1-sulfonic acid
|
|
Unsulfonated primary aromatic amines
|
Not more than 0,01% (calculated as aniline) |
|
Ether extractable matter
|
Not more than 0,2% under neutral conditions |
|
Arsenic
|
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
|
Lead
|
Not more than 10 mg/kg |
|
Mercury
|
Not more than 1 mg/Kg |
|
Cadium
|
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
|
Heavy metals (as Pb)
|
Not more than 40 mg/Kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 123 AMARANTH |
|
| Synonyms |
CI Food Red 9 |
| Definition |
Amaranth consists essentially of trisodium 2--hydroxyl-(4-sulfonato-l-naphthylazo) naphthalene-3,6-disulfonate and subsidiary colouring matters together with sodium chloride and/or sodium sulfate as the principal uncoloured components
|
|
Amaranth is described as the sodium salt. The calcium and the potassium salt are also permitted
|
| Class |
Monoazo |
|
Colour Index No
|
16185 |
|
Einecs
|
213-022-2 |
|
Chemical name
|
Trisodium 2-hydroxy-1-(4-sulfonato-1-naphthylazo) naphthalene-3,6-disulfonate |
|
Chemical formula
|
C20H11N2Na3O10S3 |
|
Molecular weight
|
604,48 |
|
Assay
|
Content not less than 85% total colouring matters, calculated as the sodium salt 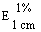 440 at ca 520 nm in aqueous solution 440 at ca 520 nm in aqueous solution
|
|
Description
|
Reddish-brown powder or granules |
| Identification |
|
|
A. Spectrometry
|
Maximum in water at ca 520 nm |
|
B. Red solution in water
|
|
| Purity |
|
|
Water insoluble matter
|
Not more than 0,2% |
|
Subsidiary colouring matters
|
Not more than 3,0% |
|
Organic compounds other than colouring matters:
|
|
|
4-aminonapththalene-1-sulfonic acid
|
 |
Total not more than 0,5%
|
|
3-hydroxynaphthalene-2,7-disulfonic acid
|
|
6-hydroxynaphthalene-2-sulfonic acid
|
|
7-hydroxynaphthalene-1,3-trisulfonic: acid
|
|
7-hydroxynaphthalene-1,3-6-trisulfonic acid
|
|
Unsulfonated primary aromatic amines
|
Not more than 0,01% (calculated as aniline) |
|
Ether extractable matter
|
Not more than 02% under neutral conditions |
|
Arsenic
|
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
|
Lead
|
Not more than 10 mg/Kg |
|
Mercury
|
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
|
Cadmium
|
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
|
Heavy metals (as Pb)
|
Not more than 40 mg/Kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 124 PONCEAU 4R, COCHINEAL RED A |
|
| Synonyms |
CI Food Red 7, New Coccine |
| Definition |
Ponceau 4R consists essentially of trisodium 2--hydroxy-1(4-sulfonato-1-naphthylazo) naphthalene-6, 8-disulfonate and subsidiary colouring matters together with sodium chloride and/or sodium sulfate as the principal uncoloured components
|
|
Ponceau 4-R is described as the sodium salt. The calcium and the potassium salt are also permitted
|
|
Class
|
Monoazo |
|
Colour Index No
|
16255 |
|
Einecs
|
220-036-2 |
|
Chemical name
|
Trisodium-2-hydroxy-1-(4-sulfonato-1-naphthylazo)--naphthalene-6,8-disulfonate |
|
Chemical formula
|
C20H11N2Na3O10S3 |
|
Molecular weight
|
604,48 |
|
Assay
|
Content not less than 80% total colouring matters, calculated as the sodium salt 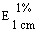 430 at ca 505 nm in aqueous solution 430 at ca 505 nm in aqueous solution
|
| Description |
Reddish powder or granules |
| Identification |
|
|
A. Spectrom-etry
|
Maximum in water at ca 505 nm |
|
B. Red solution in water
|
|
| Purity |
|
|
Water insoluble matter
|
|
|
Subsidiary colouring matters
|
Not more than 0,2% |
|
Organic compounds other than colouring matters:
|
Not more than 1,0% |
|
4-aminonaphthalene-1-sulfonic acid
|
 |
Total not more than 0,5% |
|
7-hydroxynaphthalene-1,3-disulfonic acid
|
|
3-hydroxynaphthalene-2,7-disulfonic acid
|
|
6-hydroxynaphthalene-2-sulfonic acid
|
|
7-hydroxynaphthalene-1,3,6-trisulfonic acid
|
|
Unsulfonated primary aromatic amines
|
Not more than 0,01% (calculated as aniline) |
|
Ether extractable matter
|
Not more than 0,2% under neutral conditions |
|
Arsenic
|
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
|
Lead
|
Not more than 10 mg/Kg |
|
Mercury
|
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
|
Cadmium
|
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
|
Heavy metals (as Pb)
|
Not more than 40 mg/kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 127 ERYTHROSINE |
|
| Synonyms |
CI Food Red 14 |
| Definition |
Erythrosine consists essentially of disodium 2-(2,4,5,7tetraiodo-3-oxido-6-oxoxanthen-9-yl) benzoate monohydrate and subsidiary colouring matters together with water, sodium chloride and/or sodium sulfate as the principal uncoloured components.
|
|
Erythrosine is described as the sodium salt. The calcium and the potassium salt are also permitted
|
|
Class
|
Xanthene |
|
Colour Index No
|
45430 |
|
Einecs
|
240-474-8 |
|
Chemical name
|
Disodium 2-(2,4,5,7-tetraido-3-oxido-6-oxoxanthen-9-yl) benzoate monohydrate |
|
Chemical formula
|
C20H6I4Na2O5H2O |
|
Molecular weight
|
897,88 |
|
Assay
|
Content not less than 87% total colouring matters, calculated as the anhydrous sodium salt 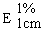 1 100 at ca 526 nm in aqueous solution at pH7 1 100 at ca 526 nm in aqueous solution at pH7
|
| Description |
Red powder or granules |
| Identification |
|
|
A. Spectrometry
|
Maximum in water at ca 526 nm at pH7 |
|
B. Red solution in water
|
|
| Purity |
|
|
Inorganic iodides calculated as sodium iodide
|
Not more than 0,1% |
|
Water insoluble matter
|
Not more than 0,2% |
|
Subsidiary colouring matters (except fluorescein)
|
Not more than 4,0% |
|
Fluorescein
|
Not more than 20 mg/kg |
|
Organic compounds other than colouring matters:
|
|
|
Tri-iodoresorcinol
|
Not more than 0,2.% |
|
2-(2,4-dihydroxy-3,5-diodobenzoyl) benzoic acid
|
Not more than 0,2% |
|
Ether extractable matter
|
From a solution of pH from 7 through 8, not more than 0,2% |
|
Arsenic
|
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
|
Lead
|
Not more than 10 mg/Kg |
|
Mercury
|
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
|
Cadmium
|
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
|
Heavy metals (as Pb)
|
Not more than 40 mg/Kg |
|
Aluminium Lakes
|
The hydrochloric acid insoluble matter method is not applicable. It is replaced by a sodium hydroxide insoluble matter, at not more than 0,5%, for this colour only
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 128 RED 2G |
|
| Synonyms |
CI Food Red 10, Azogeranine |
| Definition |
Red 2G consists essentially of disodium 8-acetamido-1-hydroxy-2-phenylazonaphthalene-3,6-disulfonate and subsidiary colouring matters together with sodium chloride and/or sodium sulfate as the principal uncoloured components
|
|
Red 2G is described as the sodium salt. The calcium and the potassium salt are also permitted |
|
Class
|
Monoazo |
|
Colour Index No
|
18050 |
|
Einecs
|
223-098-9 |
|
Chemical name
|
Disodium 8-acetamido-1-hydroxy-2-phenylazo-naphthalene-3,6-disulfonate |
|
Chemical formula
|
C18H13N3Na2O8S2 |
|
Molecular weight
|
509,43 |
|
Assay
|
Content not less than 80% total colouring matters, calculated as the sodium salt 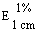 620 at ca 532 nm in aqueous solution 620 at ca 532 nm in aqueous solution
|
| Description |
Red powder or granules |
| Identification |
|
|
A. Spectrometry
|
Maximum in water at ca 532 nm |
|
B. Red solution in water
|
|
| Purity |
|
|
Water insoluble matter
|
Not more than 0,2% |
|
Subsidiary colouring matters
|
Not more than 2,0% |
|
Organic compounds other than colouring matters:
|
|
|
5-acetamido-4-hydroxynaphthalene-2,
|
 |
Total not more than 0,5% |
|
7-disulfonic acid
|
| 5-amino-4-hydroxynaphthalene-2,7-disulfonic acid |
| Unsulfonated primary aromatic amines |
Not more than 0,01% (calculated as aniline) |
|
Ether extractable matter
|
Not more than 0,2% under neutral conditions |
|
Arsenic
|
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
|
Lead
|
Not more than 10 mg/Kg |
|
Mercury
|
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
|
Cadmium
|
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
|
Heavy metals (as Pb)
|
Not more than 40 mg/Kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 129 ALLURA RED AC |
|
| Synonyms |
CI Food Red 17 |
| Definition |
Allura Red AC consists essentially of disodium 2-hydroxy-1-(2-methoxy-5-methyl-4-sulfonatophenylazo) naphthalene-6-sulfonate and subsidiary colouring matters together with sodium chloride and/or sodium sulfate as the principal uncoloured components
|
|
Allura Red AC is described as the sodium salt. The calcium and the potassium salt are also permitted
|
|
Class
|
Monoazo |
|
Colour Index No
|
16035 |
|
Einecs
|
247-368-0 |
|
Chemical name
|
Disodium 2-hydroxy-1-(2-methoxy-5-methy-4-sulfonatophenylazo) naphthalene-6-sulfonate |
|
Chemical formula
|
C18H14N2Na2O8S2 |
|
Molecular weight
|
496,42 |
|
Assay
|
Content not less than 85% total colouring matters, calculated as the sodium salt |
|
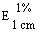 540 at ca 504 nm in aqueous solution at pH 7 540 at ca 504 nm in aqueous solution at pH 7
|
| Description |
Dark red powder or granules |
| Identification |
|
|
A. Spectrometry
|
Maximum in water at ca 504 nm |
|
B. Red solution in water
|
|
| Purity |
|
|
Water insoluble matter
|
Not more than 0,2% |
|
Subsidiary colouring matters
|
Not more than 3,0% |
|
Organic compounds other than colouring matters:
|
|
|
6-hydroxy-2-naphthalene sulfonic acid, sodium salt
|
Not more than 0,3% |
|
4-amino-5-methoxy-2-methylbenezene sulfonic acid
|
Not more than 0,2% |
|
6,6-oxybis (2-naphthalene sulfonic acid) disodium salt
|
Not more than 1,0% |
|
Unsulfonated primary aromatic amines
|
Not more than 0,01% (calculated as aniline) |
|
Ether extractable matter
|
From a solution of pH 7, not more than 0,2% |
|
Arsenic
|
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
|
Lead
|
Not more than 10 mg/kg |
|
Mercury
|
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
|
Cadmium
|
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
|
Heavy metals (as Pb)
|
Not more than 40 mg/Kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 131 PATENT BLUE V |
|
| Synonyms |
CI Food Blue 5 |
| Definition |
Patent Blue V consists essentially of the calcium or sodium compound of [4-(α-(4-diethylaminophenyl)-5-hydroxy-2,4-disulfophenyl-methylidene) 2,5-cyclohexadien-1-ylidene] diethylammonium hydroxide inner salt and subsidiary colouring matters together with sodium chloride and/or sodium sulfate and/or calcium sulfate as the principal uncoloured components
|
|
The potassium is also permitted |
| Class |
Triarylmethane |
| Colour Index No |
42051 |
| Einecs |
222-573-8 |
| Chemical names |
The calcium or sodium compound of [4-(α-(4-diethylaminophenyl)-5-hydroxy-2,4-disulfophenyl-methylidene),-2,5-cyclohexadien-1-ylidene] diethyl-ammonium hydroxide inner salt |
| Chemical formula |
Calcium compound: C27H31N2O7S2Ca½ |
|
Sodium Compound; C27H31N2O7S2Na |
| Molecular weight |
Calcium compound: 579,72 |
|
Sodium compound: 582,67 |
| Assay |
Content not less than 85% total colouring matters, calculated as the sodium salt |
|
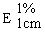 2 000 at ca 638 nm in aqueous solution at pH5 2 000 at ca 638 nm in aqueous solution at pH5
|
| Description |
Dark-blue powder or granules |
| Identification |
|
|
A. Spectrometry
|
Maximum in water at 638 nm at pH5 |
|
B. Blue solution in water
|
|
| Purity |
|
|
Water insoluble matter
|
Not more than 0,2% |
|
Subsidiary colouring matters
|
Not more than 2,0% |
|
Organic compounds other than colouring matters:
|
|
|
3-hydroxy benzaldehyde
|
 |
Total not more than 0,5% |
|
3-hydroxy benzoic acid
|
|
3-hydroxy-4-sulfobenzoic acid
|
|
N,N-diethylamino benzene sulfonic acid
|
|
Leuco base
|
Not more than 4,0% |
|
Unsulfonated primary aromatic amines
|
Not more than 0,01% (calculated as aniline) |
|
Ether extractable matter
|
From a solution of pH 5 not more than 0,2% |
|
Arsenic
|
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
|
Lead
|
Not more than 10 mg/kg |
|
Mercury
|
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
|
Cadmium
|
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
|
Heavy metals (as Pb)
|
Not more than 40 mg/kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 132 INDIGOTINE, INDIGO CARMINE |
|
| Synonyms |
CI Food Blue 1 |
| Definition |
Indigotine consists essentially of a mixture of disodium 3,3'dioxo-2,2'-bi-indolylidene-5,5'-disulfonate, and disodium 3,3'-dioxo-2,2'-bi-indolylidene-5,7'-disulfonate and subsidiary colouring matters together with sodium chloride and/or sodium sulfate as the principal uncoloured components.
|
|
Indigotine is described as the sodium salt. The calcium and the potassium salt are also permitted.
|
|
Class
|
Indigoid |
|
Colour Index No
|
73015 |
|
Einecs
|
212-728-8 |
|
Chemical names
|
Disodium 3,3'-dioxo-2,2'-bi-indolylidene-5,5'-disulfonate |
|
Chemical formula
|
C16H8N2Na2O8S2 |
|
Molecular weight
|
466,36 |
|
Assay
|
Content not less than 85% total colouring matters, calculated as the sodium salt; disodium 3,3'-dioxo-2,2' bi-indolylidene-5,7'-disulfonate: not more than 18%
|
|
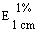 480 at ca 610 nm in aqueous solution 480 at ca 610 nm in aqueous solution
|
| Description |
Dark-blue powder or granules |
| Identification |
|
|
A. Spectrometry
|
Maximum in water at ca 610 nm |
|
B Blue solution in water
|
|
| Purity |
|
|
Water insoluble matter
|
Not more than 0,2% |
|
Subsidiary colouring matters
|
Excluding disodium 3,3'dioxo-2,2'-bi-indolylidene-5,7'-disulfonate: not more than 1,0% |
|
Organic compounds other than colouring matters:
|
|
|
Isatin-5-sulfonic acid
|
 |
Total not more than 0,5% |
|
5-sulfoanthranilic acid
|
|
Anthranilic acid
|
|
Unsulfonated primary aromatic amines
|
Not more than 0,01% (calculated as aniline) |
|
Ether extractable matter
|
Not more than 0,2% under neutral conditions |
|
Arsenic
|
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
|
Lead
|
Not more than 10 mg/Kg |
|
Mercury
|
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
|
Cadmium
|
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
|
Heavy metals (as Pb)
|
Not more than 40 mg/Kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 133 BRILLIANT BLUE FCF |
|
| Synonyms |
CI Food Blue 2 |
| Definition |
Brilliant Blue FCF consists essentially of disodium α-(4-(N-ethyl-3-sulfonatobenzylamino) phenyl)-α-(4-N-ethyl-3-sulfonatobenzylamino) cyclohexa-2,5-dienylidene) toluene-2-sulfonate and its isomers and subsidiary colouring matters together with sodium chloride and/or sodium sulfate as the principal uncoloured components.
|
|
Brilliant Blue FCF is described as the sodium salt. The calcium and the potassium salt are also permitted.
|
|
Class
|
Triarylmethane |
|
Colour Index No
|
42090 |
|
Einecs
|
223-339-8 |
|
Chemical names
|
Disodium α-(4-(N-ethyl-3-sulfonatobenzylamino) phenyl) α-(4-N-ethyl-3-sulfonatobenzylamino) cyclohexa-2,5-dienylidene) toluene-2-sulfonate. |
|
Chemical formula
|
C37H34N2 Na2O9 S3 |
|
Molecular weight
|
792,84 |
|
Assay
|
Content not less than 85% total colouring matters, calculated as the sodium salt |
|
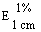 1 630 at ca 630 nm in aqueous solution 1 630 at ca 630 nm in aqueous solution
|
| Description |
reddish-blue powder or granules |
| Identification |
|
| A. Spectrometry |
Maximum in water at ca 630 nm |
| B. Blue solution in water |
|
| Purity |
|
|
Water insoluble matter
|
Not more than 0,2% |
|
Subsidiary colouring matters
|
Not more than 6,0% |
|
Organic compounds other than colouring matters;
|
|
|
Sum of 2,3-and 4-formyl benzene sulfonic acids
|
Not more than 1,5% |
|
3-((ethyl)(4-sulfophenyl amino)methyl benzene sulfonic acid
|
Not more than 0,3% |
|
Leuco base
|
Not more than 5,0% |
|
Unsulfonated primary aromatic amines
|
Not more than 0,01 % (calculated as aniline) |
|
Ether extractable matter
|
Not more than 0,2% at pH7 |
|
Arsenic
|
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
|
Lead
|
Not more than 10 mg/kg |
|
Mercury
|
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
|
Cadmium
|
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
|
Heavy metals (as Pb)
|
Not more than 40 mg/kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 140 (i) CHLOROPHYLLS |
|
| Synonyms |
CI Natural Green 3, Magesium Chlorophyll, Magnesium Phaeophytin |
| Definition |
Chlorophylls are obtained by solvent extraction of natural strains of edible plant material, grass, lucerne and nettle. During the subsequent removal of solvent, the naturally present co-ordinated magnesium may be wholly or partly removed from the chlorophylls to give the corresponding phaeophytins. The principal colouring matters are the phaeophytins and magnesium chlorophylls. The extracted product, from which the solvent has been removed, contains other pigments such as carotenoids as well as oils, fats and waxes derived from the source material. Only the following solvents may be used for the extraction: acetone, methyl ethyl ketone, dichloromethane, carbon dioxide, methanol, ethanol, propan-2-ol and hexane. |
| Class |
Porphyrin |
| Colour Index No |
75810 |
| Einecs |
Chlorophylls: 215-800-7, Chlorophyll a: 207-536-6, Chlorophyll b: 208-272-4 |
| Chemical names |
The major colouring principles are: |
|
Phytyl(132-R,17S,18S)-3)(8-ethyl-132- methoxycarbonyl-2,7,12,18-tetramethyl-13'-oxo-3-vinyl-131-132-17,18-tetrahydrocyclopenta [at]-porphyrin-17-yl] propionate, (Pheophytin a), or as the magnesium complex (Chlorophyll a) Phytyl (132-R,17S, 18S)-3-(8-ethyl-7-formyl-132-methoxycarbonyl-2, l2, 18-trimethyl-13'-oxo-3-vinyl-131-132-17,18-tetrahydrocyclopenta [at]-porphyrin-17-yl) propionate, (Pheophytin b), or as the magnesium complex (Chlorophyll b) |
| Chemical formula |
Chlorophyll a (magnesium complex): C55H72 MgN4O5 |
|
Chlorophyll a: C55H74N4O5 |
|
Chlorophyll b (magnesium complex): C55H70 MgN4O6 |
|
Chlorophyll b: C55H72N4O6 |
| Molecular weight |
Chlorophyll a (magnesium complex): 893,51 |
|
Chlorophyll a: 871,22 |
|
Chlorophyll b (magnesium complex): 907,49 |
|
Chlorophyll b: 885,20 |
| Assay |
Content of total combined Chlorophylls and their magnesium complexes is not less than 10% 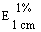 700 at ca 409 nm in chloroform 700 at ca 409 nm in chloroform
|
| Description |
Waxy solid ranging in colour from olive green to dark green depending on the content of coordinated magnesium |
| Identification |
|
| Spectrometry |
Maximum in chloroform at ca 409 nm |
| Purity |
Acetone |
 |
Not more than 50 mg/kg, singly or in combination |
| Solvent residues |
Methyl Ethyl ketone |
|
Methanol |
|
Ethanol |
|
Propan-2-ol |
|
Hexane |
|
Dichloromethane: Not more than 10 mg/kg |
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
| Lead |
Not more than 10 mg/kg |
| Mercury |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Cadmium |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Heavy metals (as Pb) |
Not more than 40 mg/kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 140 (ii) CHLOROPHYLLINS |
|
| Synonyms |
CI Natural Green 5, Sodium Chlorophyllin, Potassium Chlorphyllin |
| Definition |
The alkali salts of chlorophyllins are obtained by the saponification of a solvent extract of natural strains of edible plant material, grass, lucerne and nettle. The saponification removes the methyl and phytol ester groups and may partially cleave the cyclopentenyl ring. The acid groups are neutralized to form the salts of potassium and/or sodium. |
|
Only the following solvents may be used for the extraction: acetone, methyl ethyl ketone, dichloromethane, carbon dioxide, methanol, ethanol, propan-2-ol and hexane. |
| Class |
Porphyrin |
| Colour Index No |
75815 |
| Einecs |
287-483-3 |
| Chemical names |
The major colouring principles in their acid forms are: |
|
--3-(10-carboxylato-4-ethyl-1,3,5,8-tetramethyl-9-oxo-2-vinylphorbin-7-yl) propionate (chlorophyllin a) and |
|
--3-(10-carboxylato-4-ethyl-3-formyl-1,5,8-trimethyl-9-oxo-2-vinylphorbin-7-yl) propionate (chlorophyllin b)
Depending on the degree of hydrolysis the cyclopentenyl ring may be cleaved with the resultant production of a third carboxyl function.
|
|
Magnesium complexes may also be present. |
| Chemical formula |
Chlorophyllin a (acid form): C34H34N4O5 |
|
Chlorophyllin b (acid form): C34H32N4O6 |
| Molecular weight |
Chlorophyllin a: 578,68 |
|
Chlorophyllin b: 592,66 |
|
Each may be increased by 18 daltons if the cyclopentenyl ring is cleaved. |
| Assay |
Content of total chlorophyllins is not less than 95% of the sample dried at ca 100°C for 1 hour. |
|
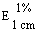 700 at ca 405 nm in aqueous solution at pH9 700 at ca 405 nm in aqueous solution at pH9
|
|
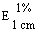 140 at ca 653 nm in aqueous solution at pH 9 140 at ca 653 nm in aqueous solution at pH 9
|
| Description |
Dark green to blue/black powder |
| Identification |
|
| Spectrometry |
Maximum in aqueous phosphate buffer at pH 9 at ca 405 nm and at ca 653 nm |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 140 (ii) CHLOROPHYLLINS--contd. |
|
| Purity |
|
| Solvent residues |
Acetone |
 |
Not more than 50 mg/kg, singly or in combination |
|
Methyl Ethyl ketone |
|
Methanol |
|
Ethanol |
|
Propan-2-ol |
|
Hexane |
|
Dichloromethane: Not more than 10 mg/kg |
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
| Lead |
Not more than 10 mg/kg |
| Mercury |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Cadmium |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Heavy metals (as Pb) |
Not more than 40 mg/kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 141 (i) COPPER COMPLEXES OF CHLOROPHYLLS |
|
| Synonyms |
CI Natural Green 3, Copper Chlorophyll, Cooper Phaeophytin |
| Definition |
Copper chlorophylls are obtained by addition of a salt of copper to the substance obtained by solvent extraction of natural strains of edible plant material, grass, lucerne, and nettle. The product, from which the solvent has been removed, contains other pigments such as carotenoids as well fats and waxes derived from the source material. The principal colouring matters are the copper phaeophytins. Only the following solvents may be used for the extraction: acetone, methyl ethyl ketone, dichloromethane, carbon dioxide, methanol, ethanol, propan-2-ol and hexane. |
| Class |
Porphyrin |
| Colour Index No |
75815 |
| Einecs |
Copper chlorophyll a: 239-830-5; copper chlorophyll b: 246-020-5 |
| Chemical names |
[Phytyl (132R, 17S, 18S]-3(-8-ethyl-132methoxycarbonyl-2,7,12,18-tetramethyl-13'-oxo-3-vinyl-131-132-17,18-tetrahydrocyclopenta [at]-porphyrin-17-yl)propionate] copper (II) (Copper Chlorophyll a) [Phytyl (132R, 17S, 18S)-3-(8-ethyl-7-formyl-132-methoxycarbonyl-2,-12,18-trimethyl-13'-oxo-3-vinyl-13113217,18-tetrahydrocyclopenta[at]-porphyrin-17-yl)propionate] copper (II) (Copper chlorphyll b) |
| Chemical formula |
Copper chlorophyll a: C55H72 Cu N4O5 |
|
Copper chlorophyll b: C55H70Cu N4O6 |
| Molecular weight |
Copper chlorophyll a: 932,75 |
|
Copper chlorophyll b: 946,73 |
|
Content to total copper chlorophylls is not less than 10% |
| Assay |
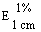 540 at ca 422 nm in chloroform 540 at ca 422 nm in chloroform
|
|
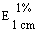 300 at ca 652 nm in chloroform 300 at ca 652 nm in chloroform
|
| Description |
Waxy solid ranging in colour from blue green to dark green depending on the source material |
| Identification |
|
| Spectrometry |
Maximum in chloroform at ca 422 nm and at ca 652 nm |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 141 (i) COPPER COMPLEXES OF CHLOROPHYLLS--contd. |
|
| Purity |
|
| Solvent residues |
Acetone |
 |
Not more than 50 mg/kg, singly or in combination |
|
Methyl Ethyl ketone |
|
Methanol |
|
Ehtanol |
|
Propan-2-ol |
|
Hexane |
|
Dichloromethane: Not more than 10 mg/kg |
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
| Lead |
Not more than 10 mg/kg |
| Mercury |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Cadmium |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Copper ions |
Not more than 200 mg/kg |
| Total copper |
Not more than 8.0% of the total copper phaeophytins |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 141 (ii) COPPER COMPLEXES OF CHLOROPHYLLINS |
|
| Synonyms |
Sodium Copper Chlorophyllin, Potassium Copper Chlorophyllin, CI Natural Green 5 |
| Definition |
The alkali salts of copper chlorophyllins are obtained by the addition of copper to the product obtained by the saponification of a solvent extraction of natural strains of edible plant material, grass, lucerne, and nettle; the saponification removes the methyl and phytol ester groups and may partially cleave the cyclopentenyl ring. After addition of copper to the purified chlorophyllins, the acid groups are neutralised to form the salts of potassium and/or sodium.
Only the following solvents may be used for the extraction: acetone, methyl ethyl ketone, dichloromethane, carbon dioxide, methanol, ethanol, propan-2-ol and hexane.
|
| Class |
Porphyrin |
| Colour Index No. |
75815 |
| Einecs |
|
| Chemical names |
The major colouring principles in their acid forms are 3-(10-Carboxylato-4-4ethyl-1, 3, 5, 8-tetramethyl-9-oxo-2-vinylphorbin-7-yl) propionate, copper complex (Copper chlorophyllin a) and 3-(10-Carboxylato-4-ethyl-3-formyl-1, 5, 8-trimethyl-9-oxo-2-vinylphorbin-7-yl) propionate, copper complex (Copper chlorophyllin b) |
| Chemical formula |
Copper chlorophyllin a (acid form: C34H32 Cu N4O5 |
|
Copper chlorophyllin b (acid form: C34H32 Cu N4O6 |
| Molecular formula |
Copper chlorophyllin a: 640,20 |
|
Copper chlorophyllin b: 654,18 |
|
Each may be increased by 18 daltons if the cyclopentenyl ring is cleaved. |
|
Content of total copper chlorophyllins is not less than 95% of the sample dried at 100°C for 1 hr. |
| Assay |
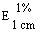 565 at ca 405 nm in aqueous phosphate buffer at pH 7,5 565 at ca 405 nm in aqueous phosphate buffer at pH 7,5
|
|
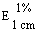 145 at ca 603 nm in aqueous phosphate buffer at pH 7,5 145 at ca 603 nm in aqueous phosphate buffer at pH 7,5
|
| Description |
Dark green to blue/black powder |
| Identification |
|
| Spectrometry |
Maximum in aqueous phosphate buffer at pH 7,5 at ca 405 nm and at 630 nm |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 141 (ii) COPPER COMPLEXES OF CHLOROPHYLLINS--contd. |
|
| Purity |
|
| Solvent residues |
Acetone |
 |
Not more than 50 mg/kg, singly or in combination |
|
Methyl ethyl ketone |
|
Methanol |
|
Ethanol |
|
Propan-2-ol |
|
Hexane |
|
Dichloromethane: not more than 10 mg/kg |
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
| Lead |
Not more than 10 mg/kg |
| Mercury |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Cadmium |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Copper ions |
Not more than 200 mg/kg |
| Total copper |
Not more than 8,0% of the total copper chlorophyllins |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 142 GREEN S |
|
| Synonyms |
CI Food Green 4, Brilliant Green BS |
| Definition |
Green S consists essentially of sodium N-[4-(dimethylamino) phenyl] 2-hydroxy-3, 6-disulfo-1-naphthalenyl) methylene]-2, 5-cyclohexadien-1-ylidene]-N-methylmethanaminium and subsidiary colouring matters together with sodium chloride and/or sodium sulphate as the principal uncoloured compounds. |
|
Green S is described as the sodium salt. The calcium and the potassium salt are also permitted. |
| Class |
Triarylmethane |
| Colour Index No. |
44090 |
| Einecs |
221-409-2 |
| Chemical names |
Sodium N-[4-[[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl](2-hydroxy-3,6-disulfo-1-naphthalenyl)-methylene]-2,5-cyclonexadien-1-ylidene]-N-methylmethanaminium;
Sodium 5-[4-dimethylamino-α-(4-dimethyliminocyclohexa-2,5-dienylidene)benzyl]-6-hydroxy-7-sulfonato-naphthalene-2-sulfonate (alternative chemical name).
|
| Checial formula |
C27H25N2Na O7S2 |
| Molecular weight |
576,63 |
| Assay |
Content not less than 80% total matters calculated as the sodium salt |
|
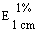 1 720 at ca 632 nm in aqueous solution 1 720 at ca 632 nm in aqueous solution
|
| Description |
Dark blue or dark green powder or granules |
| Identification |
|
| A. Spectrometry |
Maximum in water at ca 632 nm |
| B. Blue or green solution in water |
|
| Purity |
|
| Water insoluble matter |
Not more than 0,2% |
| Subsidiary colouring matters |
Not more than 1,0% |
|
Organic compounds other than colouring matters:
|
|
|
4, 4'-bis(dimethylamino)-benzhydryl alcohol
|
Not more than 0,1% |
|
4, 4'-bis(dimethylamino)-benzophenone
|
Not more than 0,1% |
|
3-hydroxynapthalene-2,7-disulfonic acid
|
Not more than 0,2% |
| Leuco base |
Not more than 5,0% |
| Unsulfonated primary aromatic amines |
Not more than 0,01% (calculated as aniline) |
| Ether extractable matter |
Not more than 0,2% under neutral conditions |
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
| Lead |
Not more than 10 mg/Kg |
| Mercury |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Cadmium |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Heavy metals (as Pb) |
Not more than 40 mg/kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 150a PLAIN CARAMEL |
|
| Definition |
Plain caramel is prepared by the controlled heat treatment of carbohydrates (commercially available food grade nutritive sweeteners which are the monomers glucose and fructose and/or polymers thereof, e.g. glucose syrups, sucrose, and/or invert syrups, and dextrose). To promote caramelisation, acids, alkalis and salts may be employed, with the exception of ammonium compounds and sulphites. |
| Einecs |
232-435-9 |
| Description |
Dark brown to black liquids or solids |
| Purity |
|
| Colour bound by DEAE cellulose |
Not more than 50% |
| Colour bound by phosphoryl cellulose |
Not more than 50% |
| Colour intensity (11) |
0,01-0,12 |
| Total nitrogen |
Not more than 0,1% |
| Total sulphur |
Not more than 0,2% |
| Arsenic |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Lead |
Not more than 2 mg/kg |
| Mercury |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Cadmium |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Heavy metals (as Pb) |
Not more than 25 mg/kg1 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 15Ob CAUSTIC SULPHITE CARAMEL |
|
| Definition |
Caustic sulphite caramel is prepared by the controlled heat treatment of carbohydrates (commercially available food grade nutritive sweeteners which are the monomers glucose and fructose and/or polymers thereof, e.g. glucose syrups, sucrose, and/or invert syrups, and dextrose) with or without acids or alkalis, in the presence of sulphite compounds (sulphurous acid, potassium sulphite, potassium bisulphite, sodium sulphite and sodium bisulphite); no ammonium compounds are used. |
| Einecs |
232-435-9 |
| Description |
Dark brown to black liquids or solids |
| Purity |
|
| Colour bound by DEAE cellulose |
More than 50% |
| Colour intensity (1) |
0,05--0,13 |
| Total nitrogen |
Not more than 0,3%(2) |
| Sulphur dioxide |
Not more than 0,2% (2) |
| Total sulphur |
0,3--3,5% (2) |
| Sulphur bound by DEAE cellulose |
More than 40% |
| Absorbance ratio of colour bound by DEAE |
19--34 |
| cellulose |
|
| Absorbance ratio (A 280/560) |
Greater than 50 |
| Arsenic |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Lead |
Not more than 2 mg/kg |
| Mercury |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Cadmium |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Heavy metals (as Pb) |
Not more than 25 mg/kg |
|
|
|
(1) Colour intensity is defined as the absorbence of a 0,1% (w/v) solution of caramel colour solids in water in a 1 cm cell at 610 nm.
|
|
|
(2) Expressed on equivalent colour basis i.e. is expressed in terms of a product having a colour intensity of 0,1 absorbence units.
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 150c AMMONIA CARAMEL |
|
| Definition |
Ammonia caramel is prepared by the controlled heat treatment of carbohydrates (commercially available food grade nutritive sweeteners which are the monomers glucose and fructose and/or polymers thereof, e.g. glucose syrups, sucrose, and/or invert syrups, and dextrose) with or without acids or alkalis, in the presence of ammonium compounds (ammonium hydroxide, ammonium carbonate, ammonium hydrogen carbonate and ammonium phosphate); no sulphite compounds are used. |
| Einecs |
232-435-9 |
| Description |
Dark brown to black liquids or solids |
| Purity |
|
| Colour bound by DEAE cellulose |
More than 50% |
| Colour bound by phosphoryl cellulose |
More than 50% |
| Colour intensity (1) |
0,08-0,36 |
| Ammoniacal nitrogen |
Not more than 0,3% (2) |
| 4-methylimidazole |
Not more than 250 mg/kg (2) |
| 2-acetyl-4-tetrahydroxy-butylimidazole |
Not more than 10 mg/kg (2) |
| Total sulphur |
Not more than 0,2% (2) |
| Total nitrogen |
0,7-3,3% (2) |
| Absorbance ratio of colour bound by phosphoryl cellulose |
13-35 |
| Arsenic |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Lead |
Not more than 2 mg/kg |
| Mercury |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Cadmium |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Heavy metals (as Pb) |
Not more than 25 mg/kg |
|
|
|
(1) Colour intensity is defined as the absorbence of a 0,1% (w/v) solution of caramel colour solids in water in a 1 cm cell at 610 nm.
|
|
|
(2) Expressed on equivalent colour basis i.e. is expressed in terms of a product having a colour intensity of 0,1 absorbence units.
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 150d SULPHITE AMMONIA CARAMEL |
|
| Definition |
Sulphite ammonia caramel is prepared by the controlled heat treatment of carbohydrates (commercially available food grade nutritive sweeteners which are the monomers glucose and fructose and/or polymers thereof (e.g. glucose syrups, sucrose, and/or invert syrups, and dextrose) with or without acids or alkalis, in the presence of both sulphite and ammonium compounds (sulphurous acid, potassium sulphite, potassium bisulphite, sodium sulphite, sodium bisulphite, ammonium hydroxide, ammonium carbonate, ammonium hydrogen carbonate, ammonium phosphate, ammonium sulphate, ammonium sulphite and ammonium hydrogen sulphite) |
| Einecs |
232-435-9 |
| Description |
Dark brown to black liquids or solids |
| Purity |
|
| Colour bound by DEAE cellulose |
More than 50% |
| Colour intensity (1) |
0,10-0,60 |
| Ammoniacal nitrogen |
Not more than 0,6% (2) |
| Sulphur dioxide |
Not more than 0,2% (2) |
| 4-methylimidazole |
Not more than 250 mg/kg(2) |
| Total nitrogen |
0,3-1,7% (2) |
|
Total sulphur
|
0,8-2,5% (2) |
|
Nitrogen/sulphur ratio of alcohol precipitate
|
0,7--2,7 |
|
Absorbance ratio of alcohol precipitate (1)
|
8--14 |
| Absorbance ratio (A280/560) |
Not more than 50 |
| Arsenic |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Lead |
Not more than 2 mg/kg |
| Mercury |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Cadmium |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Heavy metals (as Pb) |
Not more than 25 mg/kg1 2 (2) Expressed on equivalent colour basis i.e. is expressed in terms of a product having a colour intensity of 0,1 absorbance units.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 151 BRILLIANT BLACK BN, BLACK PN |
|
| Synonyms |
CI Food Black 1 |
| Definition |
Brilliant Black BN consists essentially of tetrasodium-4-acetamido-5-hydroxy-6-[7-sulfonato-4-(4-sulfonatophenylazo)-1-naphthylazo] naphthalene-1,7-disulfonate and subsidiary colouring matters together with sodium chloride and/or sodium sulfate as the principal uncoloured components. |
|
Brilliant Black BN is described as the sodium salt. The calcium and the potassium salt are also permitted. |
| Class |
Bisazo |
| Colour Index No. |
28440 |
| Einecs |
219-746-5 |
| Chemical names |
Tetrasodium 4-acetamido-5-hydroxy-6-[7-sulfonato-4-(4-sulfonatophenylazo]-1-naphthylazo] naphthalene-1,7-disulfonate |
| Chemical formula |
C28H17N5 Na4O14S4 |
| Molecular weight |
867,69 |
| Assay |
Content not less than 80% total colouring matters calculated as the sodium salt |
|
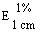 530 at ca 570 nm in solution 530 at ca 570 nm in solution
|
| Description |
Black powder or granules |
| Identification |
|
| A. Spectrometry |
Maximum in water at ca 570 nm |
| B. Black-bluish solution in water |
|
| Purity |
|
| Water insoluble matter |
Not more than 0,2% |
| Subsidiary colouring matters |
Not more than 10%(expressed on the dye content) |
|
Organic compounds other than colouring matters:
|
|
|
4-acetamido-5-hydroxynaphthalene-
|
 |
Total not more than 0,8% |
|
1,7,-disulfonic acid
|
|
4-amino-5-hydroxynaphthalene-
|
|
1,7-disulfonic acid
|
|
8-aminomphthalene-2-sulfonic acid
|
|
4,4'-diazoaminodi-(benzenesulfonic acid)
|
| Unsulfonated primary aromatic amines |
Not more than 0,01% (calculated as aniline) |
| Ether extractable matter |
Not more than 0,2% under neutral conditions |
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
| Lead |
Not more than 10 mg/Kg |
| Mercury |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Cadmium |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Heavy metals (as Pb) |
Not more than 40 mg/Kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 153 VEGETABLE CARBON |
|
| Synonyms |
Vegetable black |
| Definition |
Vegetable carbon is produced by the carbonization of vegetable material such as wood, cellulose residues, peat and coconut and other shells. The raw material is carbonized at high temperatures. It consists essentially of finely divided carbon. It may contain minor amounts of nitrogen, hydrogen and oxygen. Some moisture may be absorbed on the product after manufacture |
| Colour Index No |
77266 |
| Einecs |
215-609-9 |
| Chemical names |
Carbon |
| Chemical formula |
C |
| Molecular weight |
12,01 |
|
Content not less than 95% of carbon calculated on an anhydrous and ash-free basis |
| Assay |
Black powder, odourless and tasteless |
| Description |
|
| Identification |
|
| A. Solubility |
Insoluble in water and organic solvents |
| B. Burning |
What heated to redness it burns slowly without a flame |
| Purity |
|
| Ash (Total) |
Not more than 4,0% (ignition temperature: 625°C) |
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
| Lead |
Not more than 10 mg/kg |
| Mercury |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Cadmium |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Heavy metals (as Pb) |
Not more than 40 mg/kg |
| Polyaromatic hydrocarbons |
The extract obtained by extraction of 1 g of the product with 10 g pure cyclohexane in a continuous extraction apparatus shall be colourless, and the fluorescence of the extract in ultraviolet light shall not be more intense than that of a solution of 0,100 mg of quinine sulfate in 1,000 ml of 0,01 M sulphuric acid |
| Loss on drying |
Not more than 12% (120°C, 4 hrs) |
| Alkali soluble matter |
The filtrate obtained by boiling 2 g of the sample with 20 ml N sodium hydroxide and filtering shall be colourless |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 154 BROWN FK |
|
| Synonyms |
CI Food Brown 1 |
| Definition |
Brown FK consists essentially of a mixture of: |
|
I |
sodium 4-(2,4-diaminophenylazo) benzenesulfonate |
|
II |
sodium 4-(4,6-diamino-m-tolylazo) benzenesulfonate |
|
III |
disodium 4,4'-(4,6-diamino-1,3-phenylenebisazo)di (benzenesulfonate) |
|
IV |
disodium 4,4'-(2,4-diamino-1,3-phenylenebisazo)di (benzenesulfonate) |
|
V |
disodium 4,4'(2,4-diamino-5-methyl-1,3-phenylenebisazo)di (benzenesulfonate) |
|
VI |
trisodium 4,4',4"-(2,4-diaminobenzene-1,3,5-trisazo)tri- (benzenesulfonate) and subsidiary colouring matters together with water, sodium chloride and/or sodium sulfate as the principal uncoloured components
Brown FK is described as the sodium salt. The calcium and the potassium salt are also permitted
|
| Class |
Azo (a mixture of mono-, bis- and trisazo colours) |
| Einecs |
|
| Chemical names |
A mixture of: |
|
I |
sodium 4-(2,4-diaminophenylazo) benzenesulfonate |
|
II |
sodium 4-(4,6-diamino-m-tolylazo) benzenesulfonate |
|
III |
disodium 4,4-'(4,6-diamino-1,3-phenylenebisazo)di (benzenesulfonate) |
|
IV |
disodium 4,4'-(2,4-diamino-1,3-phenylenebisazo)di (benzenesulfonate) |
|
V |
disodium 4,4'-(2,4-diamino-5-methyl-1,3-phenylenebisazo)di (benzenesulfonate) |
|
VI |
trisodium 4,4',4"-(2,4-diaminobenzene-1.3,5-trisazo)tri-(benzenesulfonate) |
| Chemical formula |
I |
C12H11N4 NaO3S |
|
II |
C13H13N4 NaO3S |
|
III |
C18H14N6 Na2O6S2 |
|
IV |
C18H14N6 Na2O6S2 |
|
V |
C19H16N6 Na2O6S2 |
|
VI |
C24H17N8 Na3O9S3 |
| Molecular weight |
I |
314,30 |
|
II |
328,33 |
|
III |
520,46 |
|
IV |
520,46 |
|
V |
534,47 |
|
VI |
726,59 |
| Assay |
Content not less than 70% total colouring matters |
|
Of the total colouring matters present the proportions of the components shall not exceed: |
|
I |
26% |
|
II |
17% |
|
III |
17% |
|
IV |
16% |
|
V |
20% |
|
VI |
16% |
| Description |
Red-brown powder or granules |
| Identification |
|
| Orange to reddish solution |
|
| Purity |
|
| Water insoluble matter |
Not more than 0,2% |
| Subsidiary colouring matters |
Not more than 3,5% |
|
Organic compounds other than colouring matters:
|
|
|
4-aminobenzene-1-sulfonic acid m-phenylenediamine and
|
Not more than 0,7% |
|
4methyl-m-phenylenediamine
|
Not more than 0,35% |
|
Unsulfonated primary aromatic amines other than m-phenylene diamine and 4-methyl-m-phenylene diamene
|
Not more than 0,007% (calculated as aniline) |
| Ether extractable matter |
From a solution of pH7, not more than 0,2% |
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
| Lead |
Not more than 10 mg/kg |
| Mercury |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Cadmium |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Heavy metals (as Pb) |
Not more than 40 mg/kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 155 BROWN HT |
|
| Synonyms |
CI Food Brown 3 |
| Definition |
Brown HT consists essentially of disodium 4,4'-(2,4-dihydroxy-5-hydroxymethyl-1,3-phenylene bisazo) di (naphthalene-1-sulfonate) and subsidiary colouring matters together with sodium chloride and/or sulfate as the principal uncoloured components |
|
Brown HT is described as the sodium salt. The calcium and potassium salt are also permitted |
| Class |
Bisazo |
| Colour Index No |
20285 |
| Einecs |
224-924-0 |
| Chemical names |
Disodium 4,4'-(2,4-dihydroxy-5-hydroxymethyl-1,3-phenylene bisazo) di (naphthalene-l-sulfonate) |
| Chemical formula |
C27H18N4 Na2O9S2 |
| Molecular weight |
652,57 |
| Assay |
Content not less than 70% total colouring matters calculated as the sodium salt |
|
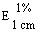 403 at ca 460 nm in aqueous solution at pH 7 403 at ca 460 nm in aqueous solution at pH 7
|
| Description |
Reddish-brown powder or granules |
| Identification |
|
| A. Spectrometry |
Maximum in water of pH 7 at ca 460 nm |
| B. Brown solution in water |
|
| Purity |
|
| Water insoluble matter |
Not more than 0,2% |
| Subsidiary colouring matters |
Not more than 10% (TLC method) |
|
Organic compounds other than colouring matters:
|
|
|
4-aminonaphthalene-1-sulfonic acid
|
Not more than 0,7% |
| Unsulfonated primary aromatic amines |
Not more than 0,01% (calculated as aniline) |
| Ether extractable matter |
Not more than 0,2% in a solution of pH 7 |
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
| Lead |
Not more than 10 mg/kg |
| Mercury |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Cadium |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Heavy metals (as Pb) |
Not more than 40 mg/kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 160a (i) MIXED CAROTENES |
|
| Synonyms |
CI Food Orange 5 |
| Definition |
Mixed carotenes are obtained by solvent extraction of natural strains of edible plants, carrots, vegetable oils, grass, alfalfa (lucerne) and nettle. |
|
The main colouring principle consists of carotenoids of which beta-carotene accounts for the major part. α-, ¾-carotene and other pigments may be present. Besides the colour pigments, this substance may contain oils, fats and waxes naturally occurring in the source material. |
|
Only the following solvents may be used in the extraction: acetone, methyl ethyl ketone, methanol, ethanol, propan-2-ol, hexane, dichloromethane and carbon dioxide |
| Class |
Carotenoid |
| Colour Index No |
75130 |
| Einecs |
230-636-6 |
| Chemical names |
|
| Chemical formula |
ß-Carotene: C40H56 |
| Molecular weight |
ß-Carotene: 536,88 |
| Assay |
Content of carotenes (calculated as ß-carotene) is not less than 5%. For products obtained by extraction of vegetables oils: not less than 0,2% in edible fats |
|
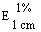 2 500 at ca 440-457 nm in cyclohexane 2 500 at ca 440-457 nm in cyclohexane
|
| Identification |
|
| Spectrometry |
Maximum in cyclohexane at 440-457 nm and 470 nm-486 nm |
| Purity |
|
| Solvent residues |
Acetone |
 |
Not more than 50 mg/kg, singly or in combination |
|
Methylethylketone |
|
Methanol |
|
Propan-2-ol |
|
Hexane |
|
Ethanol |
|
Dichloromethane: Not more than 10 mg/kg |
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
| Lead |
Not more than 10 mg/kg |
| Mercury |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Cadmium |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Heavy metals (as Pb) |
Not more than 40 mg/kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 160a (ii) BETA-CAROTENE |
|
| Synonyms |
CI Food Orange 5 |
| Definition |
These specifications apply predominantly to all trans isomer of ß-carotene together with minor amounts of other carotenoids. Diluted and stabilized preparations may have different cis/trans isomer ratios |
| Class |
Carotenoid |
| Colour Index No |
40800 |
| Einecs |
230-636-6 |
| Chemical names |
ß-Carotene, ß,ß-Carotene |
| Chemical formula |
C40H56 |
| Molecular weight |
536,88 |
| Assay |
Not less than 96% total colouring matters (expressed as ß-carotene) |
|
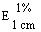 2 500 at ca 453-456 nm in cyclohexane 2 500 at ca 453-456 nm in cyclohexane
|
| Description |
Red to brownish-red crystals or crystalline powder |
| Identification |
|
| Spectrometry |
Maximum in cyclohexane at ca 453-456 nm |
| Purity |
|
| Sulphated ash |
Not more than 0,2% |
| Subsidiary colouring matters |
Carotenoids other than ß-carotene: not more than 3,0% of total colouring matters |
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
| Lead |
Not more than 10 mg/kg |
| Mercury |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Cadmium |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Heavy metals (as Pb) |
Not more than 40 mg/kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 160b ANNATTO, BIXIN, NORBIXIN |
|
| Synonyms |
CI Natural Orange 4 |
| Definition |
|
| Class |
Carotenoid |
| Colour Index No |
75120 |
| Einecs |
Annatto: |
215-735-4, annatto seed extract: 289-561-2; bixin: 230-248-7 |
| Chemical names |
Bixin: |
6'-Methylhydrogen-9'-cis-6,6'-diapocarotene-6,6-dioate |
|
|
6'-Methylhydrogen-9'-trans-6,6-diapocarotene-6,6'-dioate |
|
Norbixin: |
9'Cis-6,6'-diapocarotene-6,6'-dioic acid |
|
|
9'-Trans-6,6-'diapocarotene-6-6'-dioic acid |
| Chemical formula |
Bixin: |
C25H30O4 |
|
Norbixin: |
C24H28O4 |
| Molecular weight |
Bixin: |
394,51 |
|
Norbixin: |
380,48 |
| Description |
Reddish-brown powder, suspension or solution |
| Identification |
|
| Spectrometry |
Bixin: maximum in chloroform at ca 502 nm
Norbixin: maximum in dilute KOH solution at ca 482 nm
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
E 160b ANNATTO, BIXIN, NORBIXIN--contd.
|
|
|
(i) SOLVENT EXTRACTED BIXIN AND NORBIXIN
|
|
| Definition |
Bixin is prepared by the extraction of the outer coating of the seeds of the annatto tree (Bixa orellana L.) with one or more of the following solvents: acetone, methanol, hexane or dichloromethane, carbon dioxide followed by the removal of the solvent |
|
Norbixin is prepared by hydrolysis by aqueous alkali of the extracted bixin Bixin and norbixin may contain other materials extracted from the annatto seed. |
|
The bixin powder contains several coloured components, the major single one being bixin, which may be present in both cis- and trans- forms. Thermal degradation products of bixin may also be present. |
|
The norbixin powder contains the hydrolysis product of bixin, in the form of the sodium or potassium salts as the major colouring principle. Both cis- and trans-forms may be present |
| Assay |
Content of bixin powders not less than 75% total carotenoids calculated as bixin |
|
Content of norbixin powders not less than 25% total carotenoids calculated as norbixin |
|
Bixin: 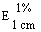 2 870 at ca 502 nm in chloroform 2 870 at ca 502 nm in chloroform
|
|
Norbixin: 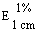 2 870 at ca 482 nm in KOH solution 2 870 at ca 482 nm in KOH solution
|
| Purity |
|
| Solvent residues |
Acetone |
 |
Not more than 50 mg/kg, singly or in combination |
|
Methanol |
|
Hexane |
|
Dichloromethane: Not more than 10 mg/kg |
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
| Lead |
Not more than 10 mg/kg |
| Mercury |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Cadmium |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Heavy metals (as Pb) |
Not more than 40 mg/kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 160b ANNATTO, BIXIN, NORBIXIN--contd. |
|
| (ii) ALKALI EXTRACTED ANATTO |
|
| Definition |
Water soluble annatto is prepared by extraction with aqueous alkali (sodium or potassium hydroxide) of the outer coating of the seeds of the annatto tree (Bixa orellana L) Water soluble annatto contains norbixin, the hydrolysis product of bixin, in the form of the sodium or potassium salts, as the major colouring principle. Both cis- and trans- forms may be present |
| Assay |
Contains not less than 0,1% of total carotenoids expressed as norbixin |
|
Norbixin: 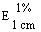 2 870 at ca 482 nm in KOH solution 2 870 at ca 482 nm in KOH solution
|
| Purity |
|
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
| Lead |
Not more than 10 mg/kg |
| Mercury |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Cadmium |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Heavy metals (as Pb) |
Not more than 40 mg/kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 160b ANNATTO, BIXIN, NORBIXIN--contd. |
|
| (iii) OIL EXTRACTED ANNATTO |
|
| Definition |
Annatto extracts in oil, as solution or suspension, are prepared by extraction of the outer coating of the seeds of the annatto tree (Bixa orellana L.) with edible vegetable oil. Annatto extract in oil contains several coloured components, the major single one being bixin, which may be present in both cis- and trans-forms. Thermal degradation products of bixin may also be present |
| Assay |
Contains not less than 0,1% of total carotenoids expressed as bixin |
|
Bixin: 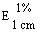 2 870 at ca 502 nm in chloroform 2 870 at ca 502 nm in chloroform
|
| Purity |
|
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
| Lead |
Not more than 10 mg/kg |
| Mercury |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Cadmium |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Heavy metals (as Pb) |
Not more than 40 mg/kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 160c PAPRIKA EXTRACT, CAPSANTHIN, CAPSORUBIN |
|
| Synonyms |
Paprika Oleoresin |
| Definition |
Paprika extract is obtained by solvent extraction of the natural strains of paprika, which consists of the ground fruits pods, with or without seeds, of Capsicum annuum L., and contains the major colouring principles of this spice. The major colouring principles are capsanthin and capsorubin. A wide variety of other coloured compounds is known to be present. |
|
Only the following solvents may be used in the extraction: methanol, ethanol, acetone, hexane, dichloromethane, ethyl acetate and carbon dioxide |
| Class |
Carotenoid |
| Einecs |
Capsanthin: 207-364-1, capsorubin: 207-425-2 |
| Chemical names |
Capsanthin: (3R, 3'S, 5'R)-3,3',-dihydroxy-ß,k-carotene-6--one |
|
Capsorubin: (3S, 3'S, 5R, 5R')3,3'dihydroxy-k,k-carotene-6,6'-dione |
| Chemical formula |
Capsanthin: C40H56O3 |
|
Capsorubin: C40H56O4 |
| Molecular weight |
Capsanthin: 584,85 |
|
Capsorubin: 600,85 |
| Assay |
Paprika extract: content not less than 7,0% carotenoids |
|
Capsanthin/capsorubin: not less than 30% of total carotenoids |
|
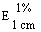 2 100 at ca 462 nm in acetone 2 100 at ca 462 nm in acetone
|
| Description |
Dark-red viscous liquid |
| Identification |
|
| A. Spectrometry |
Maximum in acetone at ca 462 nm |
| B. Colour reaction |
A deep blue colour is produced by adding one drop of sulfuric acid to one drop of sample in 2-3 drops of chloroform |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 160c PAPRIKA EXTRACT, CAPSANTHIN, CAPSORUBIN--contd. |
|
| Purity |
Ethyl acetate |
 |
Not more than 50 mg/kg, singly or in combination |
| Solvent residues |
Methanol |
|
Ethanol |
|
Acetone |
|
Hexane |
|
Dichloromethane: Not more than 10 mg/kg |
| Capsaicin |
Not more than 250 mg/kg |
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
| Lead |
Not more than 10 mg/kg |
| Mercury |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Cadmium |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Heavy metals (as Pb) |
Not more than 40 mg/kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 160d LYCOPENE |
|
| Synonyms |
Natural Yellow 27 |
| Definition |
Lycopene is obtained by solvent extraction of the natural strains of red tomatoes (Lycopersicon esculentum L.) with subsequent removal of the solvent. Only the following solvents may be used: dichloromethane, carbon dioxide, ethyl acetate, acetone, propan-2-ol, methanol, ethanol, hexane. The major colouring principle of tomatoes is lycopene, minor amounts of other carotenoid pigments may be present. Beside the other colour pigments the product may contain oils, fats, waxes, and flavour components naturally occurring in tomatoes. |
| Class |
Carotenoid |
| Colour Index No |
75125 |
| Chemical names |
Lycopene, ψ,ψ-carotene |
| Chemical formula |
C40H56 |
| Molecular weight |
536,85 |
| Assay |
Content not less than 5% total colouring matters |
|
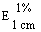 3 450 at ca 472 nm in hexane 3 450 at ca 472 nm in hexane
|
| Description |
Dark red viscous liquid |
| Identification |
|
| Spectrometry |
Maximum in hexane at ca 472 nm |
| Purity |
|
| Solvent residues |
Ethyl acetate |
 |
Not more than 50 mg/kg, singly or in combination |
|
Methanol |
|
Ethanol |
|
Acetone |
|
Hexane |
|
Propan-2-ol |
|
Dichloromethane: Not more than 10 mg/kg |
| Sulphated ash |
Not more than 0,1% |
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
| Lead |
Not more than 10 mg/kg |
| Mercury |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Cadmium |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Heavy metals (as Pb) |
Not more than 40 mg/kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 160e BETA-APO-8'-CAROTENAL (C30) |
|
| Synonyms |
CI Food Orange 6 |
| Definition |
These specifications apply to predominantly all trans isomer of ß-apo-8'-carotenal together with minor amounts of other carotenoids. Diluted and stabilized forms are prepared from ß-apo-8'-carotenal meeting these specifications and include solutions or suspensions of ß-apo-8' carotenal in edible fats or oils, emulsions and water dispersible powders. These preparations may have different cis/trans isomer ratios. |
| Class |
Carotenoid |
| Colour Index No |
40820 |
| Einecs |
214-171-6 |
| Chemical names |
ß-P-Apo-8'-carotenal, Trans-ß-apo-8' carotene-aldehyde |
| Chemical formula |
C30H40O |
| Molecular weight |
416,65 |
| Assay |
Not less than 96% of total colouring matters |
|
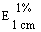 2 640 at 460--462 nm in cyclohexane 2 640 at 460--462 nm in cyclohexane
|
| Description |
Dark violet crystals with metallic lustre or crystalline powder |
| Identification |
|
| Spectrometry |
Maximum in cyclohexane at 460-462 nm |
| Purity |
|
| Sulphated ash |
Not more than 0,1% |
| Subsidiary colouring matters |
Carotenoids other than ßapo8'-carotenal: not more than 3,0% of total colouring matters |
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
| Lead |
Not more than 10 mg/kg |
| Mercury |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Cadmium |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Heavy metals (as Pb) |
Not more than 10 mg/kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 160f ETHYL ESTER OF BETA -APO-8'-CAROTENOIC ACID (C30) |
|
| Synonyms |
CI Food Orange 7, ß-apo-8'-carotenoic ester |
| Definition |
These specifications apply to predominantly all trans isomer of ß-apo-8'-carotenoic acid ethyl ester together with minor amounts of other carotenoids. Diluted and stabilised forms are prepared from ß-apo-8'-carotenoic acid ethyl ester meeting these specifications and include solutions or suspensions of ß-apo-8'-carotenoic acid ethyl ester in edible fats or oils, emulsions and water dispersible powders. These preparations may have different cis/trans isomer ratios. |
| Class |
Carotenoid |
| Colour Index No |
40825 |
| Einecs |
214-173-7 |
| Chemical names |
ß-Apo-8'-carotenoic acid ethyl ester, ethyl 8'-apo-ß-caroten-8'-oate |
| Chemical formula |
C32H44O2 |
| Molecular weight |
460,70 |
| Assay |
Not less than 96% of total colouring matters |
|
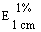 2 550 at ca 449 nm in cyclohexane 2 550 at ca 449 nm in cyclohexane
|
| Description |
Red to violet-red crystals or crystalline powder |
| Identification |
|
| Spectrometry |
Maximum in cyclohexane at ca 449 nm |
| Purity |
|
| Sulphated ash |
Not more than 0,1% |
| Subsidiary colouring matters |
Carotenoids other than ß-apo-8'-carotenoic acid ethyl ester: not more than 3,0% of total colouring matters |
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
| Lead |
Not more than 10 mg/kg |
| Mercury |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Cadmium |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Heavy metals (as Pb) |
Not more than 40 mg/kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 161b LUTEIN |
|
| Synonyms |
Mixed Carotenoids, Xanthophylls |
| Definition |
Lutein is obtained by solvent extraction of the natural strains of edible fruits and plants, grass, lucerne (alfalfa) and tagetes erecta. The main colouring principle consists of carotenoids of which lutein and its fatty acid esters account for the major part. Variable amounts of carotenes will also be present. Lutein may contain fats, oils and waxes naturally occurring in the plant material |
|
Only the following solvents may be used for the extraction: methanol, ethanol, propan-2--ol, hexane, acetone, methyl ethyl ketone, dichloromethane and carbon dioxide |
| Class |
Carotenoid |
| Einecs |
204-840-0 |
| Chemical names |
3,3'-dihydroxy-d-carotene |
| Chemical formula |
C40H56O2 |
| Molecular weight |
568,88 |
| Assay |
Content of total colouring matter not less than 4% calculated as lutein |
|
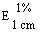 2 550 at ca 445 nm in chloroform/ethanol (10+90) or in hexane/ethanol/acetone (80 + 10 + 10) 2 550 at ca 445 nm in chloroform/ethanol (10+90) or in hexane/ethanol/acetone (80 + 10 + 10)
|
| Description |
Dark, yellowish brown liquid |
| Identification |
|
| Spectrometry |
Maximum in chloroform/ethanol (10 + 90) at ca 445 nm |
| Purity |
|
| Solvent residues |
Acetone |
 |
Not more than 50 mg/kg, singly or in combination |
|
Methyl ethyl ketone |
|
Methanol |
|
Ethanol |
|
Propan-2-ol |
|
Hexane |
|
Dichloromethane: not more than 10 mg/kg |
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
| Lead |
Not more than 10 mg/Kg |
| Mercury |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Cadmium |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Heavy metals (as Pb) |
Not more than 40 mg/Kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 161g CANTHAXANTHIN |
|
| Synonyms |
CI Food Orange 8 |
| Definition |
These specifications apply to predominantly all trans isomers of canthaxanthin together with minor amounts of other carotenoids. Diluted and stabilized forms are prepared from canthaxanthin meeting these specifications and include solutions or suspensions of canthaxanthin in edible fats or oils, emulsions and water dispersible powders. These preparations may have different cis/trans isomer ratios. |
| Class |
Carotenoid |
| Colour Index No |
40850 |
| Einecs |
208-187-2 |
| Chemical names |
ß-Carotene-4,4'-dione, canthaxanthin, 4,4'--dioxo-ß-carotene |
| Chemical formula |
C40H52O2 |
| Molecular weight |
564,86 |
| Assay |
Not less than 96% of total colouring matters (expressed as canthaxanthin) |
|
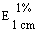 2 200 at ca 485 nm in chloroform 2 200 at ca 485 nm in chloroform
|
|
at 468--472 nm in cyclohexane |
|
at 464--467 nm in petroleum ether |
| Description |
Deep violet crystals or crystalline powder |
| Identification |
|
| Spectrometry |
Maximum in chloroform at ca 485 nm |
|
Maximum in cyclohexane at 468--472 nm |
|
Maximum in petroleum ether at 464---467 nm |
| Purity |
|
| Sulphated ash |
Not more than 0,1% |
| Subsidiary colouring matters |
Carotenoids other than canthaxanthin: Not more than 5,0% of total colouring matters |
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
| Lead |
Not more than 10 mg/kg |
| Mercury |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Cadmium |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Heavy metals (as Pb) |
Not more than 40 mg/kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 162 BEETROOT RED, BETANIN |
|
| Synonyms |
Beet Red |
| Definition |
Beet red is obtained from the roots of natural strains of red beets (Beta vulgaris L. var. rubra) by pressing crushed beet as press juice or by aqueous extraction of shredded beet roots and subsequent enrichment in the active principle. The colour is composed of different pigments all belonging to the class betalaine. The main colouring principle consists of betacyanins (red) of which betanin accounts for 75--95%. Minor amounts of betaxanthin (yellow) and degradation products of betalaines (light brown) may be present. |
|
Besides the colour pigments the juice or extract consists of sugars, salts, and/or proteins naturally occurring in red beets. The solution may be concentrated and some products may be refined in order to remove most of the sugars, salts and proteins |
| Class |
Betalaine |
| Einecs |
231-628-5 |
| Chemical names |
(S-(R',R')-4-(2-(2-Carboxy-5-(ß-D-glycilolsglucopyranosyloxy)-2,3-dihydro-6-hydroxy-1H-indol-l-yl)-ethenyl)-2,3-dihydro-2,6-pyridine-dicarboxylic acid; 1-(2-(2,6-dicarboxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-4-pyridylidene)ethylidene)-5-ß-D-glucopyranosyloxy)-6-hydroxyindolium-2-carboxylate |
| Chemical formula |
Betanin: C24H26N2O13 |
| Molecular weight |
550,48 |
| Assay |
Content of red colour (expressed as betanine) is not less than 0,4% |
|
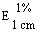 1 120 at ca 535 nm in aqueous solution at pH 5 1 120 at ca 535 nm in aqueous solution at pH 5
|
| Description |
Red or dark red liquid, paste, powder or solid |
| Identification |
|
| Spectrometry |
Maximum in water of pH 5 at ca 535 nm |
| Purity |
|
| Nitrate |
Not more than 2 g nitrate anion/g of red colour (as calculated from assay) |
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
| Lead |
Not more than 10 mg/kg |
| Mercury |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Cadmium |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Heavy metals (as Pb) |
Not more than 40 mg/kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 163 ANTHOCYANINS |
|
| Definition |
Anthocyanins are obtained by extraction with sulphited water, acidified water, carbon dioxide, methanol or ethanol from the natural strains of vegetables and edible fruits. Anthocyanins contain common components of the source material, namely anthocyanine, organic acids, tannins, sugars, minerals, etc., but not necessarily in the same proportions as found in the source material |
| Class |
Anthocyanin |
| Einecs |
208-438-6 (cyanidin); 205-125-6 (peonidin); 208-4-370 (delphinidin); 211-403-8 (malvidin); 205-127-7 (pelargonidin) |
| Chemical names |
3,3',4',5,7- Pentahydroxy-flavylium chloride (cyanidin) |
|
3,4',5,7-Tetrahydroxy-3'-methoxyflavylium chloride (peonidin) |
|
3,4',5,7,-Tetrahydroxy-3',5'-dimethoxyflavylium chloride (malvidin) |
|
3,5,7-Trihydroxy-2-(3,4,5,trihydroxyphenyl)--1-benzopyrylium chloride (delphinidin) |
|
3,3'4',5,7 Pentanydroxy-5'-methoxyflavylium chloride (petunidin) |
|
3,5,7-Trihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)--1-benzopyrilium chloride (pelargonidin) |
| Chemical formula |
Cyanidin: C15H11O6C1 |
|
Peonidin: C16H13O6C1 |
|
Malvidin: C17H15O7C1 |
|
Delphinidin: C15 H 11O7C1 |
|
Petunidin: C16H13O7C1 |
|
Pelargonidin: C15H11O5C1 |
| Molecular weight |
Cyanidin: 322,6 |
|
Peonidin: 336,7 |
|
Malvidin: 366,7 |
|
Delphinidin: 340,6 |
|
Petunidin: 352,7 |
|
Pelargonidin: 306,7 |
| Assay |
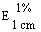 300 for the pure pigment at 515--535 nm at pH3,0 300 for the pure pigment at 515--535 nm at pH3,0
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 163 ANTHOCYANINS--contd. |
|
| Description |
Purplish-red liquid, powder or paste, having a slight characteristic odour |
| Identification |
|
| Spectrometry |
Maximum in methanol with 0,01% conc. HC1 |
|
Cyanidin: 535 nm |
|
Peonidin: 532 nm |
|
Malvidin: 542 nm |
|
Delphinidin: 546 nm |
|
Petunidin: 543 nm |
|
Pelargonidin: 530 nm |
| Purity |
|
| Solvent residues |
Methanol |
|
Not more than 50 mg/kg, singly or in combination |
|
Ethanol |
| Sulphur dioxide |
Not more than 1 000 mg/kg per percent pigment |
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
| Lead |
Not more than 10 mg/kg |
| Mercury |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Cadmium |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Heavy metals (as Pb) |
Not more than 40 mg/kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 170 CALCIUM CARBONATE |
|
| Synonyms |
CI Pigment White 18, Chalk |
| Definition |
Calcium carbonate is the product obtained from ground limestone or by the precipitation of calcium ions with carbonate ions. |
| Class |
Inorganic |
| Colour Index No. |
77220 |
| Einecs |
Calcium carbonate: 207-439-9 |
|
Limestone: 215-279-6 |
| Chemical names |
Calcium carbonate |
| Chemical formula |
CaCO3 |
| Molecular weight |
100,1 |
| Assay |
Content not less than 98% on the anhydrous basis |
| Description |
White Crystalline or amorphous, odourless and tasteless powder |
| Identification |
|
| Solubility |
Practically insoluble in water and in alcohol. Dissolves with effervescence in diluted acetic acid, in diluted hydrochloric acid and in diluted nitric acid, and the resulting solution, after boiling, give positive tests for calcium. |
| Purity |
|
| Loss on drying |
Not more than 2,0% (200°C, 4 hours) |
| Acid-insoluble substances |
Not more than 0,2% |
| Magnesium and alkali salts |
Not more than 1,5% |
| Flouride |
Not more than 50 mg/kg |
| Antimony (as Sb) |
 |
Not more than 100 mg/kg, singly or in combination |
| Copper (as Cu) |
| Chromium (as Cr) |
| Zinc (as Zn) |
| Barium (as Ba) |
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
| Lead |
Not more than 10 mg/kg |
| Cadmium |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 171 TITANIUM DIOXIDE |
|
| Synonyms |
CI Pigment White 6 |
| Definition |
Titanium Dioxide consists essentially of pure anatase titanium dioxide which may be coated with small amounts of alumina and/or silica to improve the technological properties of the product. |
| Class |
Inorganic |
| Colour Index No. |
77891 |
| Einecs |
236-675-5 |
| Chemical names |
Titanium dioxide |
| Chemical formula |
TiO2 |
| Molecular weight |
79,88 |
| Assay |
Content not less than 99% on an alumina and silica-free basis |
| Description |
Amorphous white powder |
| Identification |
|
| Solubility |
Insoluble in water and organic solvents. Dissolves slowly in hydrofluoric acid and in hot concentrated sulphuric acid. |
| Purity |
|
| Loss on drying |
Not more than 0,5% (105°C, 3 hours) |
| Loss on ignition |
Not more than 1,0% on a volatile matter free basis (800°C) |
| Aluminium oxide and/or silicon dioxide |
Total not more than 2,0% |
| Matter soluble in 0,5N HCI |
Not more than 0,5% on an alumina and silica-free basis and, in addition, for products containing alumina and/or silica, not more than 1,5% on the basis of the product as sold. |
| Water soluble matter |
Not more than 0,5% |
| Cadmium |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Antimony |
Not more than 50 mg/kg by total dissolution |
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg by total dissolution |
| Lead |
Not more than 10 mg/kg by total dissolution |
| Mercury |
Not more than 1 mg/kg by total dissolution |
| Zinc |
Not more than 50 mg/kg by total dissolution |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 172 IRON OXIDES AND IRON HYDROXIDES |
|
| Synonyms |
Iron Oxide Yellow: CI Pigment Yellow 42 and 43 |
|
Iron Oxide Red: CI Pigment Red |
|
101 and 102 |
|
Iron Oxide Black: CI Pigment |
|
Black 11 |
| Definition |
Iron oxides and iron hydroxides are produced synthetically and consist essentially of anhydrous and/or hydrated iron oxides. The range of hues includes yellows, reds, browns and blacks. Food quality iron oxides are primarily distinguished from technical grades by the comparatively low levels of contamination by other metals. This is achieved by the selection and control of the source of the iron and/or by the extent of chemical purification during the manufacturing process. |
| Class |
Inorganic |
| Colour Index No. |
Iron Oxide Yellow: 77492 |
|
Iron Oxide Red: 77491 |
|
Iron Oxide Black: 77499 |
| Einecs |
Iron Oxide Yellow: 257-098-5 |
|
Iron Oxide Red: 215-168-2 |
|
Iron Oxide Black: 235-442-5 |
| Chemical names |
Iron Oxide Yellow: hydrated ferric oxide, hydrated iron (III) oxide |
|
Iron Oxide Red: anhydrous ferric oxide, anhydrous iron (III) oxide |
|
Iron Oxide Black: ferroso ferric oxide, iron (II, III) oxide |
| Chemical formula |
Iron Oxide Yellow: FeO(OH)·xH2O |
|
Iron Oxide Red: Fe2O3 |
|
Iron Oxide Black: FeO.Fe2O3 |
| Molecular weight |
88,85: FeO (OH) |
|
159,70: Fe2O3 |
|
231,55: FeO. FeO3 |
| Assay |
Yellow not less than 60%, red and black not less than 68% total iron, expressed as iron |
| Description |
Powder; yellow, red, brown or black in hue |
| Identification |
|
| Solubility |
Insoluble in water and in organic solvents |
|
Soluble in concentrated mineral acids |
| Purity |
|
| Water soluble matter |
Not more than 1,0% |
 |
By total dissolution |
| Arsenic |
Not more than 5 mg/kg |
| Barium |
Not more than 50 mg/kg |
| Cadmium |
Not more than 5 mg/kg |
| Chromium |
Not more than 100 mg/kg |
| Copper |
Not more than 50 mg/kg |
| Lead |
Not more than 20 mg/kg |
| Mercury |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Nickel |
Not more than 200 mg/kg |
| Zinc |
Not more than 100 mg/kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 173 ALUMINIUM |
|
| Synonyms |
CI Pigment Metal, AI |
| Definition |
Aluminium powder is composed of finely divided particles of aluminium. The grinding may or may not be carried out in the presence of edible vegetable oils and/or food additive quality fatty acids. It is free from admixture with substances other than edible vegetable oils and/or food additive quality fatty acids. |
| Colour Index No. |
77000 |
| Einecs |
231-072-3 |
| Chemical names |
Aluminium |
| Chemical formula |
AI |
| Atomic weight |
26,98 |
| Assay |
Not less than 99% calculated as AI on an oil-free basis |
| Description |
A silvery grey powder or tiny sheets |
| Identification |
|
| Solubility |
Insoluble in water and in organic solvents. Soluble in dilute hydrochloric acid. The resulting solution gives positive tests for aluminium |
| Purity |
|
| Loss on drying |
Not more than 0,5% (105°C, to constant weight) |
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
| Lead |
Not more than 10 mg/kg |
| Mercury |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Cadmium |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Heavy metals (as Pb) |
Not more than 40 mg/kg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 174 SILVER |
|
| Synonyms |
Argentum, Ag |
| Class |
Inorganic |
| Colour Index No. |
77820 |
| Einecs |
231-131-3 |
| Chemical name |
Silver |
| Chemical formula |
Ag |
| Atomic weight |
107,87 |
| Assay |
Content not less than 99,5% Ag |
| Description |
Silver-coloured powder or tiny sheets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 175 GOLD |
|
| Synonyms |
Pigment Metal 3, Aurum, Au |
| Class |
Inorganic |
| Colour Index No. |
77480 |
| Einecs |
231-165-9 |
| Chemical name |
Gold |
| Chemical formula |
Au |
| Atomic weight |
197,0 |
| Assay |
Content not less than 90% Au |
| Description |
Gold-coloured powder or tiny sheets |
| Purity |
|
| Silver |
Not more than 7% |
 |
After complete dissolution |
| Copper |
Not more than 4% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 180 LITHOLRUBINE BK |
|
| Synonyms |
CI Pigment Red 57, Rubinpigment, carmine 6B |
| Definition |
Lithol Rubine BK consists essentially of calcium 3-hydroxy-4-(4-methyl-2-sulfonatophenylazo)-2-naphthalenecarboxylate and subsidiary colouring matters together with water, calcium chloride and/or calcium sulfate as the principal uncoloured components. |
| Class |
Monoazo |
| Colour Index No. |
15850:1 |
| Einecs |
226-109-5 |
| Chemical names |
Calcium 3-hydroxy-4-)4-methyl-2-sulfonatophenylazo)-2-naphthalenecarboxylate |
| Chemical formula |
C18H12 CaN2O6S |
| Molecular weight |
424,45 |
| Assay |
Content not less than 90% total colouring matters |
|
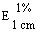 200 at ca 442 nm in dimethylformamide 200 at ca 442 nm in dimethylformamide
|
| Description |
Red powder |
| Identification |
|
| A. Spectrometry |
Maximum in dimethylformamide at ca 442 nm |
| Purity |
|
| Subsidiary colouring matters |
Not more than 0,5% |
| Organic compounds other than colouring matters: |
|
| 2 Amino-5-methylbenzene-sulfonic acid, calcium salt |
Not more than 0,2% |
| 3-hydroxy-2-naphthalenecar-boxylic acid, calcium salt |
Not more than 0,4% |
| Unsulfonated primary aromatic amines |
Not more than 0,01% (expressed as aniline) |
| Ether extractable matter |
From a solution of pH 7, not more than 0,2% |
| Arsenic |
Not more than 3 mg/kg |
| Lead |
Not more than 10 mg/kg |
| Mercury |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Cadmium |
Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Heavy metals (as Pb) |
Not more than 40 mg/kg |
|
|
|
GIVEN under the Official Seal of the Minister for Health, this 19th day of December, 1995.
|
|
|
MICHAEL NOONAN,
|
|
|
Minister for Health.
|
|
|
|
|
|
EXPLANATORY NOTE
|
|
|
These Regulations implement the Directives on food additives generally and on colours and sweeteners in particular, which are listed below.
|
|
|
Council Directive 89/107/EEC(1) on the approximation of the laws of the Member States concerning food additives authorised for use in foodstuffs intended for human consumption.
|
|
|
(1)OJ No. L40, 11.2.89, pp 27-33
|
|
|
European Parliament and Council Directive 94/35/EC(2)on sweeteners for use in foodstuffs.
|
|
|
(2)OJ No. L237, 10.9.94, pp 3-12
|
|
|
European Parliament and Council Directive 94/36/EC(3) on colours for use in foodstuffs.
|
|
|
(3)OJ No. L237, 10.9.94, pp 13-29
|
|
|
Commission Directive 95/31/EC(4) laying down specific criteria of purity concerning sweeteners for use in foodstuffs.
|
|
|
(4)OJ No. L178, 28.7.95, pp 1-19
|
|
|
Commission Directive 95/45/EC(5) laying down specific purity criteria concerning colours for use in foodstuffs.
|
|
|
(5)OJ No. L226 22.9.95, pp 1-45
|
|
|
All food additives must comply with the provisions in Part I of the Regulations while, in addition, sweeteners and colours used as food additives must comply with the provisions in Parts II and III respectively.
|
|
|
These Regulations, cited as the European Communities (General Provisions on the Control of Additives, and in particular Colours and Sweeteners for use in Foodstuffs) Regulations, 1995 come into effect on 31st December 1995.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

 : between + 90 and + 92°
: between + 90 and + 92° = + 105,5 to + 105,5° (5% w/v solution)
= + 105,5 to + 105,5° (5% w/v solution) = + 13 to + 16° calculated on the anhydrous basis (10% w/v aqueous solution)
= + 13 to + 16° calculated on the anhydrous basis (10% w/v aqueous solution) : + 14,5 to + 16,5°
: + 14,5 to + 16,5° 1 607 at ca 426 nm in ethanol
1 607 at ca 426 nm in ethanol
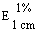 328 at ca 444 nm in aqueous solution
328 at ca 444 nm in aqueous solution In aqueous solution
In aqueous solution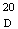 between -115° and -140° in a 0,05 N sodium hydroxide solution
between -115° and -140° in a 0,05 N sodium hydroxide solution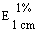 250 at ca 375 nm in aqueous solution
250 at ca 375 nm in aqueous solution In aqueous solution
In aqueous solution between +38° and +42° in a 5 molar HCI solution
between +38° and +42° in a 5 molar HCI solution 530 at ca 426 nm in aqueous solution
530 at ca 426 nm in aqueous solution
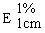 865 (principal component) at ca 411 nm in aqueous acetic acid solution
865 (principal component) at ca 411 nm in aqueous acetic acid solution
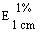 555 at ca 485 nm in aqueous solution at pH7
555 at ca 485 nm in aqueous solution at pH7
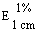 510 at ca 516 nm in aqueous solution
510 at ca 516 nm in aqueous solution
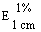 440 at ca 520 nm in aqueous solution
440 at ca 520 nm in aqueous solution
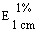 430 at ca 505 nm in aqueous solution
430 at ca 505 nm in aqueous solution
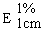 1 100 at ca 526 nm in aqueous solution at pH7
1 100 at ca 526 nm in aqueous solution at pH7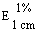 620 at ca 532 nm in aqueous solution
620 at ca 532 nm in aqueous solution
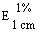 540 at ca 504 nm in aqueous solution at pH 7
540 at ca 504 nm in aqueous solution at pH 7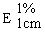 2 000 at ca 638 nm in aqueous solution at pH5
2 000 at ca 638 nm in aqueous solution at pH5
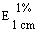 480 at ca 610 nm in aqueous solution
480 at ca 610 nm in aqueous solution
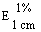 1 630 at ca 630 nm in aqueous solution
1 630 at ca 630 nm in aqueous solution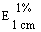 700 at ca 409 nm in chloroform
700 at ca 409 nm in chloroform
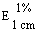 700 at ca 405 nm in aqueous solution at pH9
700 at ca 405 nm in aqueous solution at pH9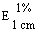 140 at ca 653 nm in aqueous solution at pH 9
140 at ca 653 nm in aqueous solution at pH 9
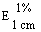 540 at ca 422 nm in chloroform
540 at ca 422 nm in chloroform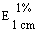 300 at ca 652 nm in chloroform
300 at ca 652 nm in chloroform
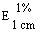 565 at ca 405 nm in aqueous phosphate buffer at pH 7,5
565 at ca 405 nm in aqueous phosphate buffer at pH 7,5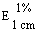 145 at ca 603 nm in aqueous phosphate buffer at pH 7,5
145 at ca 603 nm in aqueous phosphate buffer at pH 7,5
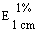 1 720 at ca 632 nm in aqueous solution
1 720 at ca 632 nm in aqueous solution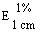 530 at ca 570 nm in solution
530 at ca 570 nm in solution
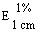 403 at ca 460 nm in aqueous solution at pH 7
403 at ca 460 nm in aqueous solution at pH 7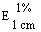 2 500 at ca 440-457 nm in cyclohexane
2 500 at ca 440-457 nm in cyclohexane
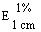 2 500 at ca 453-456 nm in cyclohexane
2 500 at ca 453-456 nm in cyclohexane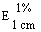 2 870 at ca 502 nm in chloroform
2 870 at ca 502 nm in chloroform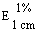 2 870 at ca 482 nm in KOH solution
2 870 at ca 482 nm in KOH solution
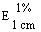 2 870 at ca 482 nm in KOH solution
2 870 at ca 482 nm in KOH solution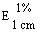 2 870 at ca 502 nm in chloroform
2 870 at ca 502 nm in chloroform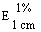 2 100 at ca 462 nm in acetone
2 100 at ca 462 nm in acetone
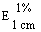 3 450 at ca 472 nm in hexane
3 450 at ca 472 nm in hexane
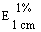 2 640 at 460--462 nm in cyclohexane
2 640 at 460--462 nm in cyclohexane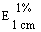 2 550 at ca 449 nm in cyclohexane
2 550 at ca 449 nm in cyclohexane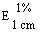 2 550 at ca 445 nm in chloroform/ethanol (10+90) or in hexane/ethanol/acetone (80 + 10 + 10)
2 550 at ca 445 nm in chloroform/ethanol (10+90) or in hexane/ethanol/acetone (80 + 10 + 10)
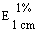 2 200 at ca 485 nm in chloroform
2 200 at ca 485 nm in chloroform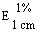 1 120 at ca 535 nm in aqueous solution at pH 5
1 120 at ca 535 nm in aqueous solution at pH 5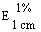 300 for the pure pigment at 515--535 nm at pH3,0
300 for the pure pigment at 515--535 nm at pH3,0
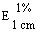 200 at ca 442 nm in dimethylformamide
200 at ca 442 nm in dimethylformamide